
What is NIST Compliance? A Complete 2025 Guide?

NIST compliance refers to adhering to the standards set by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a non-regulatory federal agency. NIST develops technologies, metrics, and standards that support innovation and enhance the economic competitiveness of U.S.-based organizations in the science and technology sectors. As part of this mission, it publishes guidelines and frameworks to help federal agencies comply with the requirements of the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA).
NIST standards bring together industry best practices and security guidelines from various publications, emphasizing scientific rigor, traceability, and continuous improvement. They are especially important for organizations that handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and must comply with regulations such as FISMA, which requires federal agencies to implement strong data protection measures.
The average cost of a data breach worldwide in 2023 was an astounding $4.45 million, and according to IBM's analysis, many of these breaches occurred as a result of inadequate security measures or noncompliance. This demonstrates the need to adhere to established standards such as NIST, which assist in reducing risk and safeguarding sensitive data. Let's delve into this article to learn more about NIST compliance, including who requires it, the main frameworks involved, and why safe company operations and data protection are so crucial in 2025.
Key Takeaways:
- Understand what NIST compliance is and why it is necessary for securing data
- Learn who must follow NIST standards, including federal agencies and contractors
- Explore key NIST frameworks like CSF, SP 800-53, and SP 800-171
- Follow a clear checklist covering risk assessment, security controls, and ongoing audits
- Discover the benefits, common challenges, and practical steps to get started with NIST compliance in 2025
What Does NIST Compliance Mean?
NIST compliance means following the cybersecurity standards and guidelines established by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a non-regulatory agency under the U.S. Department of Commerce. These standards take a risk-based approach, helping organizations adopt proven best practices to protect sensitive data, minimize threats, and strengthen overall security.
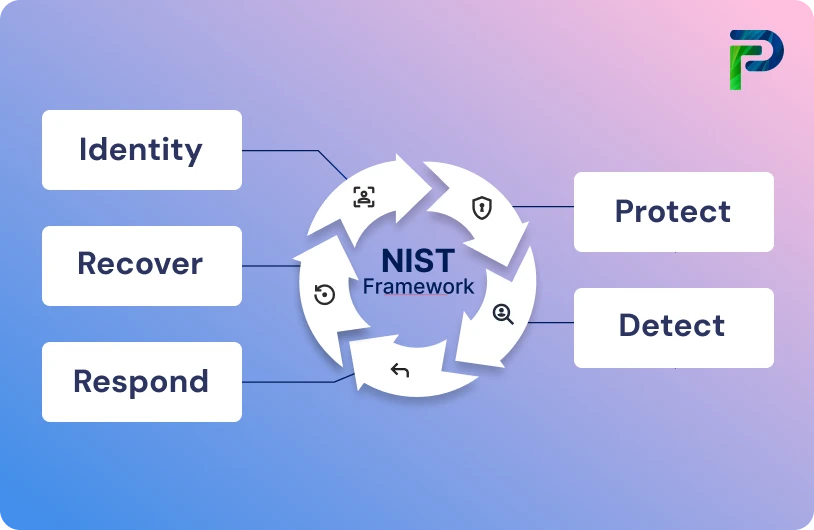
At the core of NIST’s framework are five essential functions that guide organizations through the cybersecurity lifecycle:
- Identify – Map out critical assets, risks, and potential vulnerabilities.
- Protect – Implement safeguards such as access controls, authentication, and encryption.
- Detect – Continuously monitor systems and networks to spot suspicious activity.
- Respond – Take prompt action to contain and manage incidents effectively.
- Recover – Restore normal operations quickly while learning from incidents to improve defenses.
By aligning with these principles, organizations can create a structured and resilient security posture that not only ensures compliance but also builds long-term trust and reliability.
Who Needs to Be NIST Compliant?
Any organization that works with the U.S. government is required to comply with NIST standards. This includes federal agencies, contractors, subcontractors, and even businesses planning to bid for government projects in the future. Compliance removes potential barriers during the bidding process and helps ensure eligibility.
NIST SP 800-171 – Protecting CUI
- Applies to organizations that manage or process Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
- Legally binding for companies handling sensitive government data.
- Failure to comply or self-certify can result in loss of contracts.
NIST SP 800-53 – Federal Systems
- Applies to federal agencies and government contractors that operate federal information systems.
- Ensures strong safeguards are in place to protect federal data and IT infrastructure.
- Contractors must also ensure their subcontractors are NIST-compliant to avoid risks to ongoing or future projects.
Examples of Organizations That Must Comply
Examples include defense contractors, educational institutions engaged in federal programs, financial service providers supporting government initiatives, healthcare data processors handling sensitive records, employment agencies serving federal contracts, and manufacturers supplying products to the government.
Why Private Companies Should Consider It
Even if not required, private-sector organizations are encouraged to adopt NIST standards. Doing so improves security posture, streamlines operations, and provides a competitive advantage when pursuing government contracts.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework explains all of the data protection measures required to develop a more secure organization. The framework employs a consistent method to ensure that assets are appropriately safeguarded from hostile individuals and code.
It consists of five steps:
Step 1. Identify: During this process, the data and systems that must be safeguarded are identified. This frequently includes those subject to specific legislation aimed at protecting customers, patients, or sensitive information.
Step 2. Protect: To protect the data, the team implements security measures during the protection phase. These frequently include specialized equipment, software, and tools made to handle typical security issues. To ensure that everyone can cooperate in protecting sensitive data and systems, it might also need to enlist the help of stakeholders and staff.
Step 3. Detect: In the detection process, tools and policies are meant to detect an incident as it occurs. This demands increased visibility into the organization's different systems, networks, and devices. It may also comprise apps that manage data or interact with it in the course of normal operations.
Step 4: Respond: During the response phase, a corporation must design a strategy for dealing with a danger. The strategy will detail the many approaches employed to mitigate the danger, as well as the instruments that will be used. An organization's response system may incorporate deliberate redundancies meant to attack a danger from several perspectives, such as redundant firewalls or antivirus software.
Step 5: Recover: If an attack penetrates the network, the NIST method includes steps to assist an organization in recovering as rapidly as feasible. This could include restoring data from backups, regaining control of workstations, or restarting parallel devices. Recovery may also include resiliency strategies and technologies to minimize downtime.
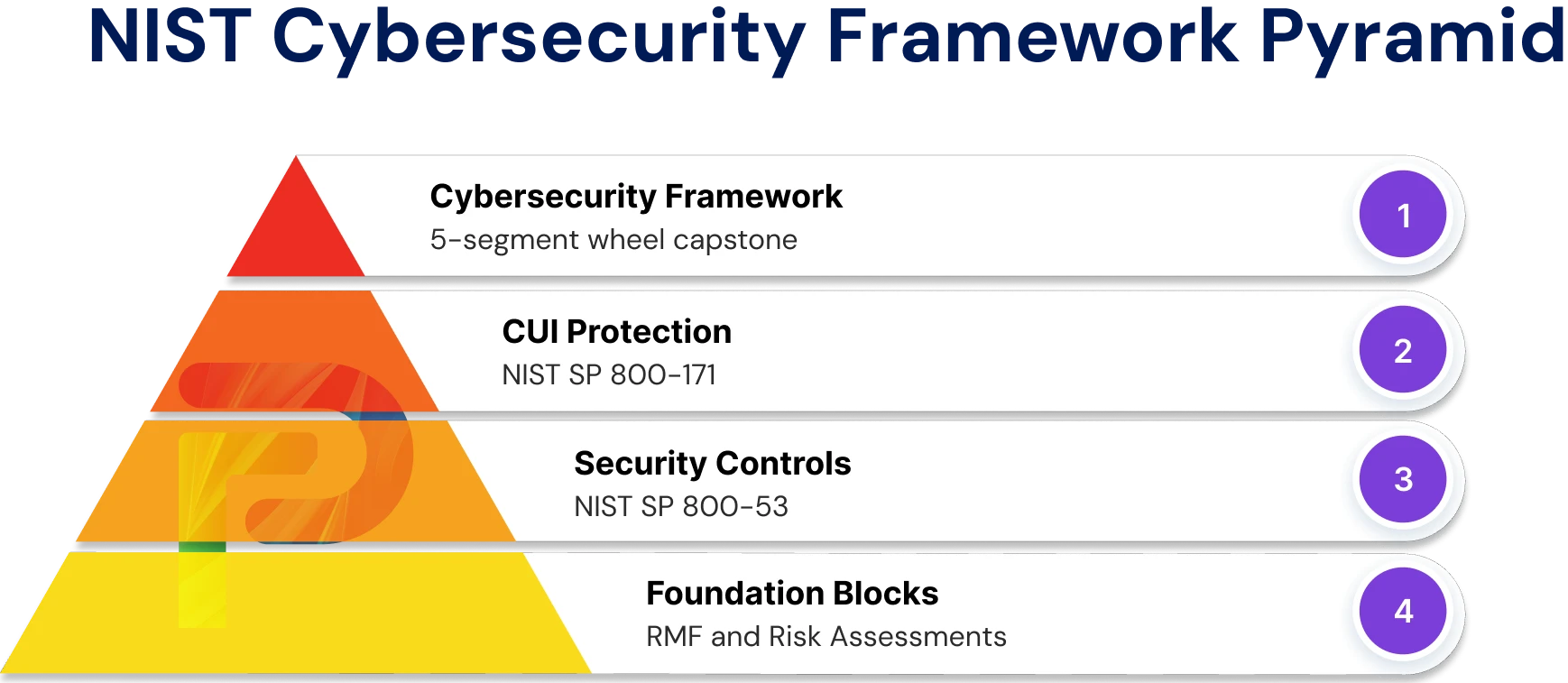
Key NIST Standards & Frameworks Explained
NIST publishes several key standards that guide how organizations protect data, manage risks, and meet compliance requirements. Below are the most important frameworks you need to know.
NIST SP 800-53
Organizations that manage federal data or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) must comply with the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA). NIST Special Publication 800-53 supports FISMA by providing a comprehensive framework of security and privacy controls.
NIST SP 800-53 establishes a structured method to protect systems and data, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information. Its catalog of controls allows organizations to address cybersecurity challenges according to risk levels and operational requirements.
NIST 800-53 Compliance Checklist
- Categorize Systems: Define the impact level of information systems on confidentiality, integrity, and availability, using FIPS 199 and NIST SP 800-60.
- Choose Controls: Apply the RMF from NIST SP 800-37 to select and tailor security controls from the 800-53 catalog based on categorization and risk.
- Deploy Controls: Implement the selected controls within your systems and operational environment.
- Evaluate Controls: Test, validate, and document results to confirm control effectiveness.
- Grant Authorization: Approve system operation once risk is determined to be acceptable.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously track controls to detect changes, identify vulnerabilities, and maintain a secure posture.
NIST SP 800-171
NIST SP 800-171 is designed to safeguard Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) in non-federal systems and organizations. Its goal is to ensure sensitive but unclassified data is properly protected, particularly for businesses that work with government agencies.
The framework establishes 14 families of security requirements, ranging from access control to incident response, creating a comprehensive approach to data protection.
NIST 800-171 Compliance Checklist
- Locate CUI: Determine where CUI exists in your environment by mapping how it is stored, processed, and transmitted.
- Assess Current Security: Compare your existing practices against the 110 security requirements of NIST 800-171 to identify weaknesses and prioritize remediation.
- Define Baseline Controls: Develop a set of tailored controls aligned with NIST 800-171 requirements to address security gaps.
- Apply Security Measures: Implement encryption, access controls, incident response, and other required safeguards to meet compliance.
- Maintain Documentation: Record security policies, procedures, and evidence of control implementation for accountability.
- Review and Improve: Continuously monitor systems, update controls, and adapt to emerging threats to sustain compliance.
Other Standards (RMF, Risk Assessments)
-
NIST SP 800-37 – Risk Management Framework (RMF)
NIST SP 800-37 introduces the Risk Management Framework (RMF), which provides a structured process for managing cybersecurity risks. The framework guides organizations in assessing systems, implementing security measures, and continuously monitoring their effectiveness. By aligning with risk management strategies, NIST 800-37 ensures that security decisions are integrated into the overall governance of information systems. -
NIST SP 800-30 – Risk Assessments
NIST SP 800-30 focuses on conducting risk assessments to support effective decision-making. It helps organizations identify threats, analyze vulnerabilities, and determine the potential impact on operations. This process allows security teams to prioritize risks and apply appropriate safeguards. Together, 800-37 and 800-30 establish a solid foundation for proactive cybersecurity and informed risk-based management.

NIST Compliance Requirements & Checklist
Achieving compliance with NIST standards requires a systematic approach to securing your organization’s assets and operations. This checklist simplifies the key steps to help you implement and maintain robust cybersecurity practices effectively:
-
Conduct a Risk Assessment Begin with a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and analyze your organization’s vulnerabilities. This involves cataloging critical assets, recognizing potential threats, and evaluating the potential impact of those threats on your business operations. The risk assessment provides a foundation to prioritize security efforts and align them with your organization’s risk tolerance.
-
Implement Security Controls Based on the risk assessment, implement appropriate security controls aligned with NIST guidelines. These include:
- Access Management: Apply the principle of least privilege, ensuring only authorized employees have access to critical systems and data.
- Encryption: Protect sensitive data in transit and at rest with strong encryption techniques.
- Endpoint Protection & Monitoring: Deploy endpoint security solutions and continuous monitoring tools that provide real-time detection of anomalies, automated alerts, and behavioral analysis.
For organizations developing software, integrating the NIST Secure Software Development Framework (SSDF) is also recommended to secure applications throughout the development lifecycle.
- Documentation & Policies Develop clear, action-oriented policies that define your incident response processes, roles, and responsibilities. Ensure your team knows exactly how to act during a cybersecurity incident, allowing for swift containment and recovery. Additionally, establish a Cybersecurity Program Management Team involving IT, security, legal, and management representatives to oversee NIST compliance efforts. Maintain thorough documentation of:
- Risk assessments
- Implemented controls
- Incident response policies
- Recovery plans
This well-organized documentation simplifies compliance audits and supports ongoing improvements.
- Ongoing Monitoring & Audits
Continuously monitor your environment to detect threats early and prevent escalation. Implement log monitoring, automated alerts, and behavioral analytics for proactive threat detection. Regularly test your recovery plans through simulated exercises to verify your team can respond efficiently during real incidents.
Perform routine internal assessments, penetration testing, and third-party audits to identify control gaps and improve security posture. Ensure third-party vendors are evaluated for compliance with your cybersecurity policies and NIST standards, and include relevant compliance clauses in vendor contracts.
Treat NIST compliance as a continuous process:
- Stay updated on NIST’s evolving guidelines.
- Revise and improve security measures regularly to address emerging cyberthreats.
This approach ensures your organization stays resilient and compliant as new challenges arise.
- Monitor and Detect Threats Strengthen defenses by actively monitoring networks and systems for suspicious behavior. Advanced monitoring solutions, combined with anomaly detection and real-time alerting, help identify potential breaches quickly, reducing the risk of serious incidents.
- Develop and Test Recovery Plans Prepare for potential disruptions with a detailed recovery plan that outlines how to restore operations after an incident. Test these plans regularly with simulated exercises to ensure your team can respond effectively under pressure.
- Maintain Comprehensive Documentation Keep detailed and organized records of security policies, implemented controls, and incident response plans. A well-documented compliance trail not only streamlines audits but also provides valuable insight for ongoing improvements.
Why NIST Compliance Matters in 2025?
In 2025, the digital landscape is more complex and connected than ever. Cyber threats are growing in sophistication, and data privacy regulations are becoming stricter worldwide. This makes NIST Compliance not just a good practice, but a strategic necessity for organizations handling sensitive data.
Enhance Data Security & Reduce Risks
NIST compliance provides a structured, tested framework of controls and best practices designed to safeguard sensitive data from cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches. By implementing these standards, organizations can significantly reduce their security risks, ensuring that critical systems remain protected against evolving threats.
Build Customer & Stakeholder Trust
Consumers, business partners, and regulatory bodies now expect organizations to demonstrate strong cybersecurity measures. Adopting NIST frameworks signals a serious commitment to security and data protection, building trust and offering a competitive edge in today’s market.
Stay Aligned with Key Regulations
NIST compliance supports alignment with major regulations, such as:
- FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act): Mandates federal agencies and contractors to implement strong cybersecurity controls based on NIST standards.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Protects patient health information and recommends NIST controls for securing health data.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Though European-focused, GDPR’s emphasis on data protection is complemented by NIST’s structured approach to safeguarding personal data.
By aligning with these regulations, organizations avoid hefty fines, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
Navigate the Complexity of Hybrid Environments
With the rise of remote work, cloud adoption, and interconnected devices, the traditional network perimeter is dissolving. NIST frameworks help organizations shift to an identity-centric security model, focusing on protecting data and systems rather than just the network boundary.
Benefits of NIST Compliance
NIST compliance brings significant advantages to organizations of all sizes. It strengthens security, reduces risks, builds trust, and helps meet regulatory requirements, making it a key strategy for modern businesses.
- Stronger Data Security At its core, NIST compliance helps organizations protect sensitive data more effectively. Whether dealing with classified or customer information, applying NIST’s structured security controls minimizes the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. These standards, originally designed to protect highly sensitive government data, now help businesses safeguard critical information and maintain customer trust.
- Risk & Breach Mitigation Following NIST guidelines empowers organizations to prevent and respond to threats like malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks more efficiently. With a solid security framework in place, companies can detect and mitigate risks faster, reduce the spread of attacks, and limit the impact of any security incident, keeping operations safer and more stable.
- Competitive Advantage & Trust Being NIST-compliant is a clear signal of reliability. It not only helps businesses qualify for government contracts involving Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) but also gives an edge over competitors. Clients and partners prefer subcontractors that follow stringent data security practices, seeing them as responsible and trustworthy, which strengthens business relationships and opens new opportunities.
- Regulatory Readiness NIST compliance simplifies meeting multiple regulatory requirements, including HIPAA and FISMA. By aligning with these standards, companies reduce the complexity of audits and avoid legal risks related to data security compliance, allowing them to focus more on business growth while staying protected.
Common Challenges in Achieving NIST Compliance
Achieving and maintaining NIST compliance is a complex process. Organizations face several challenges, including cost, ongoing monitoring, and aligning NIST with other frameworks. Here’s a closer look at these key difficulties.
- Cost & Resource Burden
It’s important to understand that the total cost of NIST compliance varies from business to business. Several factors influence the overall expense:
- Organization Size: Larger companies manage more systems, tools, and personnel, which increases the cost proportionally.
- Compliance Level: According to the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC), which extends the NIST framework, there are five compliance levels. NIST 800-171 aligns with Level 3, and higher levels require more investment in infrastructure and processes.
- Current Compliance Status: Companies already close to compliance face lower costs, while those starting from scratch, especially non-compliant organizations, tend to spend more to meet the requirements.
- CUI Access Scope: Since NIST 800-171 focuses on securing Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), only systems, tools, and personnel handling CUI need full upgrades, reducing costs for parts of the infrastructure that don’t interact with it.
-
Aligning NIST with Other Frameworks
Many organizations need to comply not just with NIST, but also with other standards such as ISO 27001, PCI DSS, and SOC 2. NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is designed to complement these standards, but mapping requirements and processes across multiple frameworks can be complex and time-consuming.To simplify this, companies often use tools like the NIST CSF Reference Tool or compliance automation solutions like Tech Prescient. These tools help integrate and compare requirements, identify gaps, and streamline the overall process, reducing manual effort and minimizing confusion when aligning NIST CSF with other standards. -
Continuous Monitoring Requirement
NIST compliance is not a one-off project; it requires ongoing effort. Organizations must regularly monitor their systems, policies, and processes to stay compliant. This involves staying updated on new regulatory requirements, evaluating emerging cybersecurity risks, performing internal audits, and responding to incidents in real time. The continuous nature of compliance management increases the workload for IT and security teams, making sustained vigilance and resource allocation essential.
Final Thoughts
NIST compliance is no longer just a regulatory checkbox; it’s a strategic investment in the security and resilience of your organization. As cyber threats continue to grow in sophistication, adopting a structured approach to compliance ensures your sensitive data stays protected, your reputation stays intact, and your business stays competitive.
At Tech Prescient, we simplify your NIST compliance journey with automated solutions, expert guidance, and practical tools. Whether you’re just starting or fine-tuning existing controls, we help you identify gaps, implement security measures, document policies, and maintain continuous monitoring, without straining your resources.
Don’t let compliance complexity hold you back or expose you to risk. Take the first step toward a stronger, more resilient cybersecurity posture with Tech Prescient today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does NIST compliance mean?
NIST compliance simply means following the security standards and guidelines created by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. These frameworks help organizations protect sensitive data, secure their systems, and reduce cyber risks. It’s about having a structured approach to cybersecurity. In short, it ensures your defenses align with trusted federal best practices.2.What are the 5 functions of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is built around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Think of it as a risk-based lifecycle for managing cybersecurity threats. Each function plays a role, from spotting risks to protecting assets, detecting incidents, responding effectively, and recovering quickly. Together, they create a holistic defense cycle.3. Who must comply with NIST standards?
By default, federal agencies and their contractors are required to comply with NIST standards. This ensures consistency and security in government-related systems. However, many private organizations also adopt these standards voluntarily. It helps them strengthen security and align with industry or regulatory requirements.4. What is the difference between NIST 800-53 and NIST 800-171?
Both are key NIST publications, but serve different needs. NIST 800-53 defines a broad set of security and privacy controls for federal information systems. On the other hand, NIST 800-171 is more focused, aiming to protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) in non-federal systems. Together, they cover different but complementary compliance areas.5. Is NIST compliance mandatory for private companies?
For private companies, NIST compliance is not legally mandatory. However, many choose to follow it because the frameworks are considered industry best practice. Adopting NIST helps strengthen cybersecurity, demonstrate responsibility to stakeholders, and often meet contractual or regulatory expectations. It’s about being proactive rather than reactive.