
What Is Identity Lifecycle Management (ILM)? Complete Guide for 2026

Identity Lifecycle Management (ILM) is the collective term for the processes and technology used to manage the identity of users and their access privileges from initial onboarding to role changes and offboarding. If an organization can perform each one of these phases in a secure and automated fashion, it helps to limit risk, enhance compliance, and streamline access to systems.
Identity Lifecycle Management (ILM) is the answer to this dilemma. It governs every step of an identity's life cycle inside your digital environment (and beyond), whether it’s provisioning, mid-life role changes, or deprovisioning.. However, this cannot simply be seen as a technical process; it must be understood as a planned and deliberate approach to identifying, connecting, and governing people, technology, and permissions within a consistent, secure environment. This forms the foundation of a secure and efficient identity and access management lifecycle.
The downside is that many organizations are still hampered by silos of IAM tools, or outdated manual processes from a predigital time, leaving opportunities for manual errors and added risk. That’s where modern ILM platforms like Identity Confluence come in, transforming access chaos into structured control through automated identity lifecycle management.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the key phases of identity lifecycle management.
- Learn about identity lifecycle management tools and automation benefits.
- Discover best practices for secure digital identity lifecycle management.
What is Identity Lifecycle Management?
Identity Lifecycle Management, or ILM, is a structured, strategic framework that is designed to manage any aspect of a digital identity's lifecycle within an organization from creation to retirement. The people and things managed under ILM can include employees, contractors, freelancers, third-party vendors and also non-human entities, like bots, APIs, and IoTs. In the increasingly complex digital world of 2025, ILM is foundational to ensuring secure and controlled access to resources across cloud platforms, physical infrastructure, and hybrid ecosystems.
Unlike traditional Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems, which primarily focus on prohibiting what access permissions are allowed for people and things, ILM takes an identity lifecycle view. It acknowledges that identities are dynamic. People come into the company, move into different roles, take on different responsibilities, and so on until they leave or get fired. In many situations, machine identities can spin up and down in as little as seconds and are able to operate at scale in cloud native or application-centric environments. ILM ensures that all of these changes are reflected in access permissions accordingly and accurately, forming a robust identity governance lifecycle.
What gives ILM its true power is matching the HR event (for example, onboarding, promotion, or termination) with the corresponding IT action (for example, provisioning or revoking access). This establishes a governance model where driven by the organization's business logic, security protocols can align, and compliance becomes a by-product of good design. This end-to-end process represents the core of the identity lifecycle management process.
We’ll unpack this even further in the next section when we examine the various identity lifecycle management phases and how they connect to form a dynamic, secure, and auditable identity management environment.
Key Phases of Identity Lifecycle Management
The identity lifecycle isn't just one event; it's a journey that every identity (human or non-human) makes across your systems. When you bring someone on board (the Joiner phase), when they change roles (the Mover phase), and when their relationship with your organization ends (the Leaver phase), each part of this journey has a direct impact on security, compliance and user experience. When organizations recognize and understand these important phases of identity lifecycle management, they can develop a straightforward, auditable, and secure identity governance lifecycle that is governed by some aspect of business logic and as it relates to reducing risk in Joiner-Mover-Leaver scenarios.
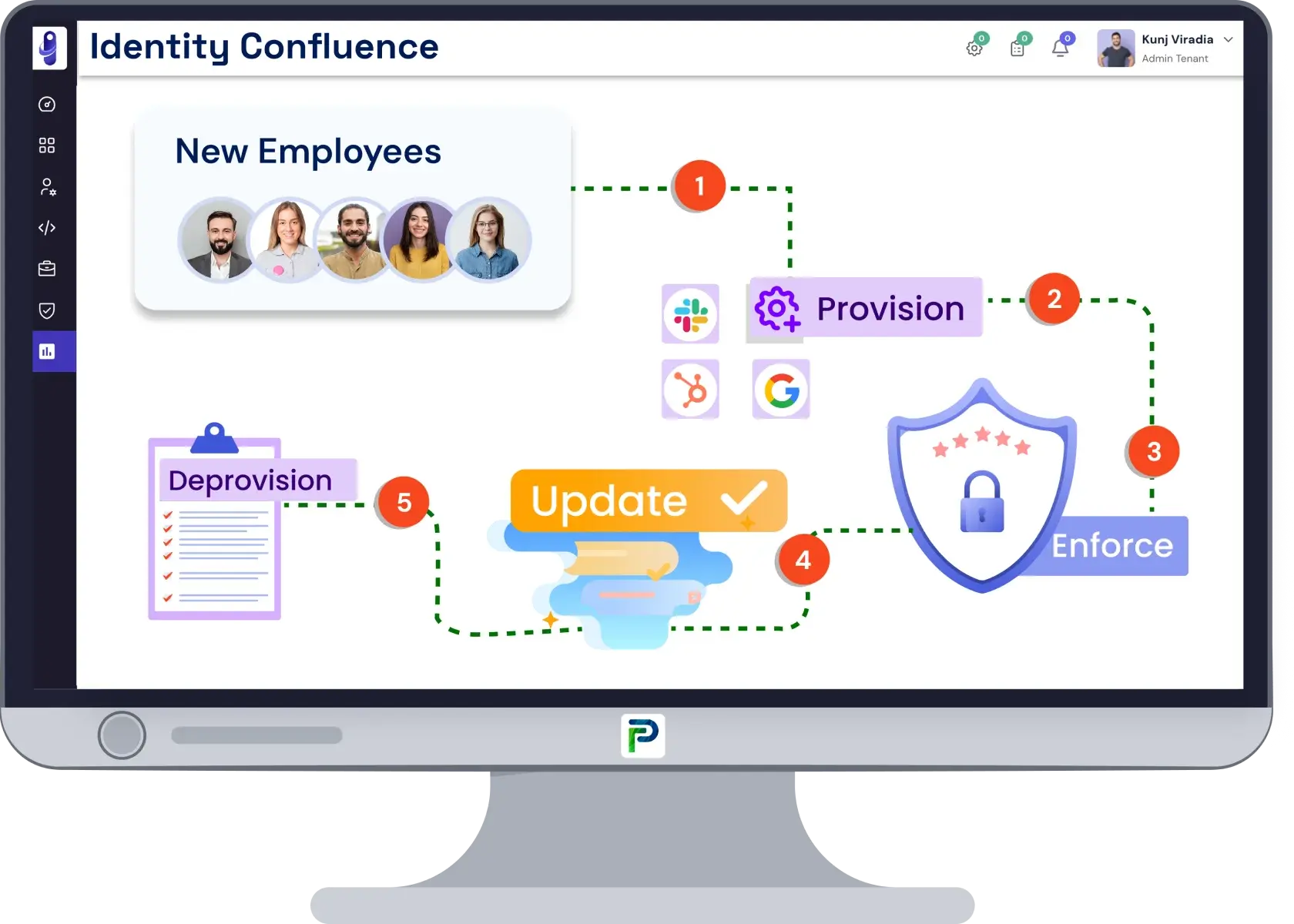
Step 1 -Identity Creation and Provisioning
This first stage will begin with a moment when a user has first been identified in the organization's HR system, typically upon a hiring or onboarding event. This is the moment the ILM platform has been activated, creating a digital identity with a unique user identifier. The user identification is more than just a username; it maps the user to a business role, job function, and department, as well as whatever additional contextual attributes are needed to make intelligent access decisions. At this stage, the system provisions what are sometimes referred to as "Birthright Access."
These are the essential tools and platforms for the individual to be able to perform the essential tasks they need to perform from day 1, like email, internal communication apps, department-specific applications, and shared drives. All of this is automated and occurs in real-time, and at no time did even a single helpdesk ticket need to be raised. This phase exemplifies effective identity provisioning and deprovisioning within a user lifecycle management strategy.
Conversational Insight: It is like giving a new employee their office badge, a laptop, and office keys on day 1, except the keys here are digital and provisioned for the employee based on their job and team.
Step 2- Identity Management and Access Control
As users progress through their tenure at an organization, their roles often change. They may join new teams, receive promotions, transfer departments, or take on temporary assignments. Each of these scenarios creates new access requirements while also removing others. If the access landscape is not actively managed, we can quickly find ourselves with overprivileged users and exposure to risk.
Modern ILM solutions address this problem by offering fine-grained access models, such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), or some combination of these. These models allow a system to modify access seamlessly for users based on updates to their profile attributes (e.g. title, department, location). The result is that access is always context-based, appropriate based on the role and aligned to business rules. This is a key part of an automated identity lifecycle management strategy.
Real-World Example: When a sales representative is promoted to regional sales manager, their permissions to an RBAC system would change automatically. They now have access to more advanced analytics dashboards, regional sales data, while access to the entry-level sales tools may be taken away (so they could not confuse their regional role with the national role).
Step 3 - Identity Modification and Role Changes
This phase covers the fluid middle ground where users require temporary access, special rights, or entitlements for project-based needs. It is also frequently where things start to go awry. Without strong controls over the lifecycle of access, users can build up access rights over time, a phenomenon known as “Access Creep.”
An advanced ILM platform mitigates this by applying automation and governing rules. It keeps track of every change in access, has those tied to business justification, and builds in time limits or review cycles. In other words, temporary access expires automatically, unless assessed or renewed. These checks are essential within a healthy user lifecycle management structure and must support Joiner-Mover-Leaver workflows.
Expert Insight: The value of automating this transition is not about making it more habitable for users – it is about compliance, and protecting your organization from insider threats or accidental data leaks. A manual spreadsheet is not going to work in 2025!
Step 4 - Identity De-provisioning and Retirement
De-provisioning is likely the most important and least acknowledged step in the identity lifecycle. When an employee leaves a company, or a contractor finishes a project, you must revoke access immediately. Delays in de-provisioning generally lead to orphaned accounts and profiles, which are not utilized, but can be exploited by malicious actors.
Identity lifecycle management (ILM) platforms are closely connected to HRMS and ticketing systems. Most ILM platforms can notify and observe termination events in real time. In the event of a termination, the ILM triggers an action to start a comprehensive deactivation program that includes all SaaS, on-prem, and cloud platforms that the user has been associated with. This allows organizations to improve their security posture and also account for licensing and compliance hygiene, reinforcing the full identity and access management lifecycle.
Pro Insight: Best-in-class ILM systems are now able to proactively monitor accounts for inactivity. If a user has not logged into an array of tools for 30, 60, or 90 days, it will note the user accounts as inactive for review, or it may automatically disable them. Using this long-tailed clean-up reduces your exposure to risk, as well as assists your audit readiness. This step is critical within the identity governance lifecycle and digital identity lifecycle protection.
Essential Identity Lifecycle Management Tools
Experts are aligned: your ILM architecture must have both coverage and flexibility. Forrester states organizations must move from the rule-based, legacy IAM approaches and bring automation driven by policy.
Recommended Tools for 2025:
- HRMS & Directory Integrations: For real-time identity triggers (e.g., Workday, SAP, AD)
- Role & Policy Engines: To assign access based on job functions and contextual rules
- Automated Provisioning Frameworks: To eliminate manual onboarding and offboarding
- Audit & Compliance Dashboards: To generate logs, reports, and certifications
- Risk-Based Intelligence: Leveraging AI/ML to flag anomalies and detect access misuse
- Self-Service Access Management: Empowering users to request or renew access with approval workflows
"A future-ready ILM platform isn’t just automated it’s adaptive, policy-driven, and aligned to business velocity." - Ian Glazer, VP Identity, Salesforce
At Tech Prescient our Identity Lifecycle Management (ILM) solution reframes how organizations manage their human and non-human identities across their digital enterprise using a modern, policy-driven approach with pre-configured automated provisioning and risk-based intelligence to reduce program governance overhead and proactively manage enterprise security and compliance risk at scale.
ILM for Non-Human Entities
With organizations moving to more digital processes, machine identities are becoming just as essential and just as dangerous as human identities. From bots and APIs to service accounts and containers, non-human entities are now powering the vast majority of backend processes. But lacking governance, they often are invisible and uncontrolled by IT teams, which can make machine identities very risky. This is why managing machine identities must be an integral aspect of an identity lifecycle management approach.
Managing Machine and Device Identities
Today's organizations are adopting automation and scaling digitally, which means non-human identity types (IoT, bots, service accounts, containers, APIs, etc) are everywhere - and generally outnumber humans in many environments. These machine identities are completing critical business functions like: transferring data, automating processes, and enabling app-to-app communications. Regardless, these machine identities are becoming an increasingly significant security and compliance risk when not managed.
In many organizations, machine identities have been excluded from IAM activity, creating gaps in visibility, orphaned credentials, and elevated privilege without governance - which adversaries will exploit. This is why ILM or Identity Lifecycle Management strategies in 2025 will require the same level of diligence and governance for non-human entities as for human identities.
An effective ILM platform should:
- Automatically create and tag machine identities: Anytime new API keys are generated for DevOps tasks or services (e.g., a new bot account to automate customer support), the process should automatically enroll the entity, ingest metadata (owner, purpose, expiration), and apply scoped access policies.
- Issue time-bound credentials and API tokens: Credentials to machine identities must also be limited in their duration (short-lived) and should be automatically rotatable. Temporary tokens should expire in hours or days depending on context, with renewal only upon validation and logging. This guarantees ephemeral access and reduces persistent exposure.
- Deactivate or archive inactive entities: Machine identities that exceed their defined inactivity period (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days) should inherently either result in an automated review or a straightforward safe removal. This action removes dormant access and therefore diminishes the risks of credential compromise.
Scenario: Assume we have a CI/CD pipeline that requires an API key to deploy a container into production. Bear in mind that it is normally inappropriate to give an API key with no expiration. An example the ILM platform would be provisioning a key that had a 72-hour expiration period, linking it to the project and logging utilization. If the project extended beyond 72 hours, the team would have to request approval for another key provisioning. Once expired, the key would be automatically revoked and archived.
Why It Matters: As cyber threats are now targeting overlooked vectors like machine accounts, it is essential to apply lifecycle governance to these non-human identities. Orphaned service accounts, hard coded credentials, and non-expiring access tokens are common funnel points during security breaches. Managing non-human identities in ILM not only closes access gaps but assures audit readiness and operational integrity across automated processes.
Benefits of Effective Identity Lifecycle Management
A successful ILM implementation isn't just a win for your IT department, it's a strategic win for your whole organization. Here is the summary of how a successful ILM system affects more enterprise performance areas:
- Enhanced Security Posture: Recognizing that we grant any access right by need to know / time not to exceed, ILM really limits our organization's attack surface. ILM limits access sprawl by strictly enforcing policies that expand or revoke access rights when users move through multiple roles or exit the organization. This greatly minimizes the likelihood of misuse or unauthorized access on the inside or outside.
- Audit Confidence Increased: Compliance is more than a checkbox exercise at an organization. An organization requires verifiable, traceable evidence of governance. ILM platforms store audit logs associated with every identity action, access grant, change, or revocation. When audit season approaches, security and compliance teams have everything necessary to demonstrate policy compliance for any piece of regulation starting with SOX through GDPR.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: With ILM, users never have to wait for IT to manually add access. Rather, everything is automated in real-time, be it provisioning on Day 1 or revoking when someone is offboarded. This means less downtime, quicker ramp-ups to productivity, and easier role transitions whether you’re moving to a different project or department.
- Reduced IT Workload: Helpdesk teams are often overwhelmed with the number of access-related requests. ILM Systems eliminate, streamline, and automate these requests so the IT team can focus on more strategic items like improving architecture, or security. When users can self-service their access request, and not wait for approval, your need for user intervention significantly reduces.
- Saved on Employee Experience: Smooth access leads to smooth workflows. Our roles have access at the right time, and no employee will waste time waiting on overly complicated approvals, or delay steps that bottleneck workflows. Pre-defined access policies are attached to roles, so users get what they need, without wasting more time and emails on additional requests or approvals. This builds and maintains trust in the IT function, along with more employee satisfaction and productivity.
Insights That Matter: ILM Platforms are not merely reactive, ILM platforms are predictive. The difference can be found with real-time dashboards surface anomalies and trends such as unused entitlements, segregation of duties (SoD) violations, and overprivileged accounts. The visibility from dashboards enables organizations to continuously monitor and better understand risk across many variables and refine access strategies around actual usage and risk patterns.
Best Practices for Implementing ILM
Deploying ILM within your organization will involve more than just turning on the switch and flipping the lever. Success requires thoughtful design, collaboration with the stakeholders, and a mindset that expects the future. Here are some best practices that will drive success and future sustainability:
- Anchor Workflows in your HRMS: Your HR system should be the system of record for identity events like onboarding, transfers, and terminations. Integrating ILM to behind the scenes systems like Workday or SAP to trigger identity change based on confirmed business processes, which is paramount. The use of your HR system eliminates three factors in the traditional access management process: manual input, reducing human error, and aligning identity governance to business change and people.
- Define and Maintain Business Roles: Moving from access management for individual user access to definitive business roles, as in let’s say ‘Sales Associate’ with policy based access to CRM, email, and sales analytics tools. When users are assigned or moved into that definitive role, their organizational role automatically updates. This role-based structure improves management efficiency and scales with your growth.
- Use Visual Policy Builders: Traditional access management policies can be buried in code or broadsheets. A visual policy builder will enable security teams, IT admins, and auditors to easily consume, review, and edit policies. Greater exercising will lead to greater transparency, quicker approval cycles, and assistance for the non-audience in following governance rules and meeting compliance obligations.
- Bring in Non-Human Identities: Machine identities (bots, IoT devices, service accounts) are often an afterthought when considering access. Machine identities also need lifecycle controls along the same parameters as a human user - autogenerated provisioning, expiration timelines, and vendor monitoring. Including substantively aligned machine identities as part of your ILM strategy ensures you're covered and minimizes sham costs.
- Automate Continuous Certification: Annual access reviews are fundamentally insufficient given today's tech-accelerated environment. Automating periodic certification campaigns -- ex. quarterly certification for 6 months of the year, provides an opportunity to review and validate access privileges on an ongoing basis. Intelligent workflows/AI functions can even notify reviewers of any anomalies and recommend revoking privileges for accounts that did not have activity in the past quarter, both models support and document compliance.
- Centralize Logging/Reporting: A mature ILM space displays a single pane of glass to view all things dispositioned by identity. This includes access, approval processes, policy rules changed, decisions made for compliance reviews etc. Centralized logging creates accountability and collectively expedites audits, compliance inquiries, and engagement with regulators. Exportable logs and audit trails are especially critical for meeting standards like SOX, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How is ILM different from traditional IAM solutions?
While IAM (identity and access management) emphasizes the facets of authentication (verifying who you are) and authorization (defining what you can access), ILM considers the entire identity lifecycle: building that identity, provisioning access, changing access when the role or department changes, and finally, securely offboarding. ILM interacts with contextual governance, workflow tasks, and auditing to ensure continued appropriate access rights throughout identity lifecycle. - If we already use SSO and MFA, why do we still need ILM?
While identifying and validating identities, via Single Sign-On (SSO), and accessing with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) are key components to the login process, these aspects do not address management access, especially when roles change over time, or a change is warranted. With ILM, entitlements will ensure business roles provide appropriate entitlements access, there is automation in the update of access, and users are immediately denied access when no longer needed. Essentially, ILM provides an operational, governance layer above SSO, MFA. - What kind of ROI can we expect from ILM implementation?
When comparing against industry benchmarks, organizations that have deployed automated ILM solutions are seeing benefits including 30-50% decreases to onboarding times, 60-70% decreases in helpdesk tickets related to access, and faster compliance work. These are all benefits that offer measurable cost savings and productivity impact. Most organizations are realizing their return on investment (ROI) between 12 and 18 months after deployment. - How does ILM handle distributed, remote, or hybrid workforces?
ILM solutions connect with cloud-native apps, HRMS systems and identity providers to help automate provisioning and de-provisioning workflows for users across geographies and time zones. Whether the user is remote, freelance, or part-time, ILM ensures the user gets the right access on day 1 and loses access immediately upon exit. Both of these capabilities are critical for compliance and cybersecurity, especially in a remote-first world.