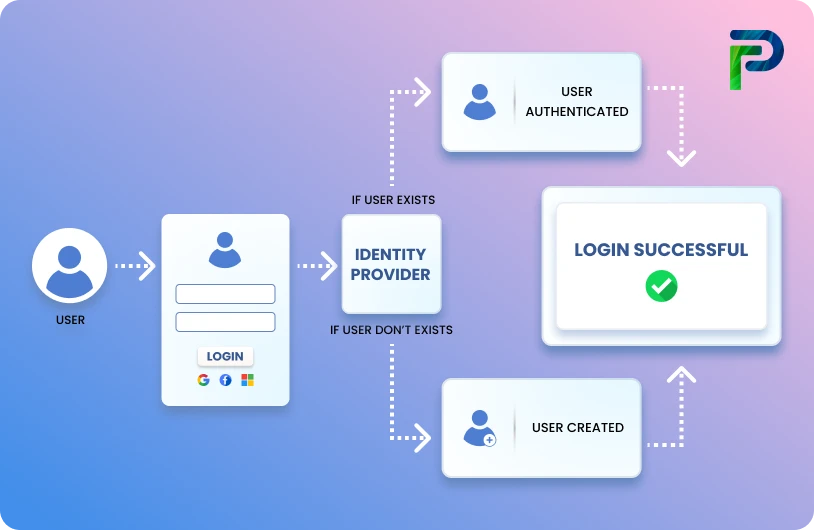
What is a User Provisioning Policy?


User provisioning policy specifies how employees automatically gain access to systems and data based on their function or department. It facilitates quicker onboarding, less manual labor, and uniform access across all applications for IT staff. Managing access gets more difficult as businesses expand, and having a clear strategy helps eliminate uncertainty and misunderstanding. Additionally, it guarantees that access remains in accordance with internal security and least privilege guidelines.
A solid user provisioning policy also guards against concerns like access creep, orphaned accounts, and compliance gaps. A clearly defined user provisioning policy acts as a framework for systematically creating, updating, and deactivating user accounts across their lifecycle. This helps maintain strong security, reduces the workload on IT teams, and avoids the mistakes that naturally happen with manual provisioning. This framework is a game-changer for IT teams that must manage many apps and identity systems.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024, access-related misconfigurations are among the top contributors to breaches, increasing overall breach costs and risk exposure. This makes it even more important for organizations to automate and standardize how user access is managed. In the rest of this blog, we’ll break down how a user provisioning policy works, the key components you need, and best practices to design one effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- A user provisioning policy automates access to systems and data based on roles or departments.
- Organizations need it to prevent unauthorized access, reduce errors, and stay compliant.
- Core components include role-based access control, onboarding automation, access changes, deprovisioning, security, and audits.
- It works by automating the user lifecycle from account creation to role updates and deprovisioning.
- Benefits include faster onboarding, stronger security, easier audits, and best practices to ensure scalability.
Why Organizations Need a User Provisioning Policy
A user provisioning policy gives organizations a structured, compliant, and consistent way to manage access across systems like Identity Manager Server, Windows NT servers, Solaris servers, and other managed resources. It defines which accounts, entitlements, and attributes users are allowed to have, either through requests or automatic role-based provisioning. These policies prevent unauthorized privileges, reduce access sprawl, and strengthen overall security posture. They also serve as a foundation for meeting regulatory and audit requirements.
This is why every organization needs a strong provisioning policy:
1. Prevents Access Creep and Orphaned Accounts
Provisioning policies ensure that all accounts and entitlements are authorized, monitored, and aligned with role requirements.
Identity Manager evaluates every access request against the policy and can:
- Flag or mark accounts as noncompliant
- Suspend unauthorized accounts
- Alert administrators to revoke disallowed privileges
- Automatically correct misaligned access
2. Ensures Employees Have the Right Access From Day One
Policies define the general information, membership, and entitlements that govern account creation. They also support role-based provisioning, enabling automatic assignment of required accounts and access the moment a user joins a role or business unit. This reduces onboarding delays and guarantees consistent access across all service types, service instances, and service selection policies.
3. Meets Compliance Standards Like SOX, GDPR, and HIPAA
Provisioning policies act as a compliance control by enforcing approved access paths. Additional capabilities include:
- Mapping policies to business units with specific scope levels
- Applying join directives when multiple policies impact the same user
- Using Identity Manager APIs to generate audit-ready access data
Administrators can create, modify, preview, draft, commit, or delete provisioning policies, ensuring continuous compliance throughout the identity lifecycle.
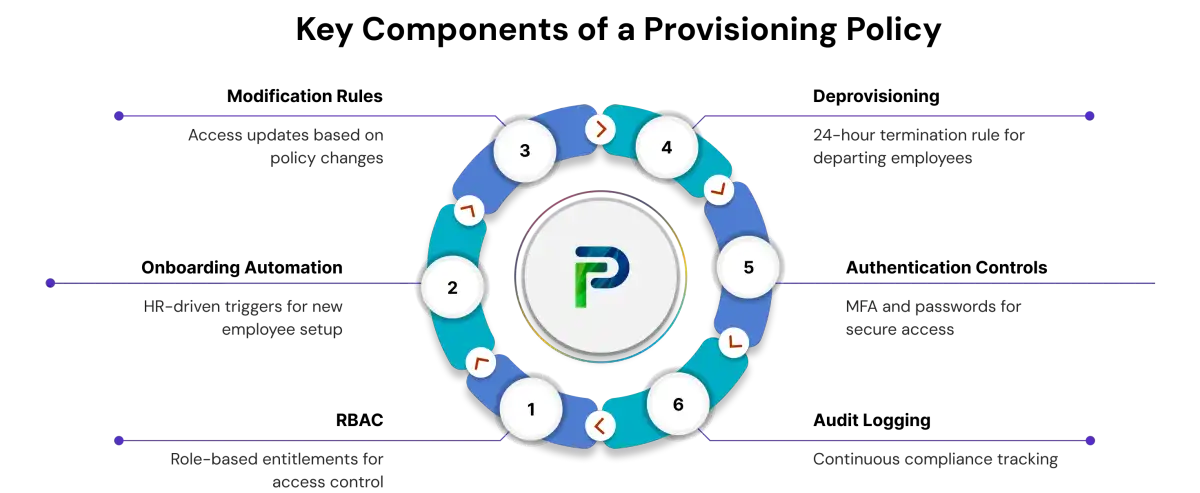
Key Components of a User Provisioning Policy
Every user access provisioning policy includes these six foundational elements that define how access is assigned, managed, secured, and audited across the organization.
1. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control is the backbone of a user provisioning policy because it assigns access based on defined job roles, departments, and responsibilities. By mapping entitlements, service instances, and account permissions to each role, organizations enforce least privilege and avoid over-provisioning.
To illustrate:
- Marketing team members receive access to CRM platforms and campaign management tools
- Finance team members receive access to ERP systems, accounting applications, and financial reporting dashboards
RBAC also supports scalability by ensuring access automatically aligns with organizational structure and business unit hierarchy.
2. Onboarding Automation
Automated onboarding links HR triggers to provisioning workflows so new users receive the right general information, membership, and entitlements immediately. When HR adds a new employee or contractor, Identity Manager automatically provisions approved accounts across Windows NT servers, Solaris servers, cloud services, and other managed resources.
This eliminates manual setup delays, reduces errors, and ensures employees have the required access on day one.
3. Modification Rules
Modification rules define how access changes when an employee’s role, department, or business unit shifts. These rules rely on policy parameters, join directives, and service selection policies to adjust entitlements without manual intervention.
In typical scenarios:
- Access is automatically upgraded when a user is promoted
- Sensitive permissions are removed when employees transfer to new teams
- Entitlements are recalculated when attributes in the identity profile change
Clear modification rules reduce security gaps and maintain consistent access hygiene throughout the user lifecycle.
4. Deprovisioning Procedures
Effective deprovisioning ensures access is revoked quickly and accurately. A user provisioning policy must outline steps to disable or delete accounts across all service types and service instances within a defined SLA, typically within 24 hours of employee exit.
Key steps generally involve:
- Removing accounts created by the provisioning policy
- Revoking entitlements from user identity profiles
- Ensuring no orphaned accounts remain in any target system
This minimizes insider risk and maintains compliance with organizational security policies.
5. Authentication and Security Controls
Authentication standards are a crucial component of a user provisioning policy. These controls ensure only authorized users can access sensitive systems and data.
A strong policy incorporates:
- Multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
- Password complexity rules to enforce strong and unique passwords for all users.
- Conditional access that restricts login based on device type, network, or location.
- Support for biometric or smart-card authentication where required.
Regular audits of authentication methods to maintain compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS.
6. Compliance and Audit Logging
Compliance and audit capabilities ensure that access changes are documented and traceable. Identity Manager APIs and audit logs capture:
- Who received access
- When access was granted, modified, or revoked
- Which provisioning policy authorized the change
These logs support regulatory requirements, internal audits, and security investigations. Documenting the provisioning policy itself also ensures clarity, accountability, and consistent enforcement across IT, HR, and security teams.
How a User Provisioning Policy Works (Step-by-Step)
A user provisioning policy works by automating the complete user lifecycle across the organization. It uses predefined rules to determine who gets access, how that access is updated, and when it is removed. This ensures consistency, security, and compliance for every user account created or modified.
Here is how the process typically functions in a real environment
1. Rule Creation
Assessing organizational needs and requirements is the foundation of rule creation. This involves understanding how the company operates, which systems each department uses, and what access employees require. By evaluating these needs, the organization can create role-based access criteria that align with security, compliance, and productivity goals. This reduces the chances of access mismatches, duplicate permissions, or unnecessary privileges.
2. Policy Assignment
Defining user roles and responsibilities plays an important part in this step. Once roles are created, the user provisioning policy is assigned to specific HR groups or departments. When HR assigns a job title, the system immediately knows what access to grant. This keeps user permissions aligned with the principle of least privilege and ensures that access reflects job duties accurately. It also makes audits easier since each permission is tied to a documented role.
3. Automated Provisioning
Establishing access control mechanisms ensures that the system can automatically create accounts and grant entitlements. Group-based permissions, predefined access levels, and controlled resource allocation help the system provision new users without manual effort. This increases efficiency and reduces errors. It also ensures that new employees receive all necessary access on their first day in the organization.
4. Access Updates
Determining authentication protocols becomes important when a user’s role or department changes. Multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, smart card authentication, or other approved methods verify identity during access updates. These authentication standards keep the environment secure while permissions are recalculated. They also help organizations meet regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI DSS.
5. Deprovisioning
Documenting the policy ensures that the deprovisioning process is predictable, secure, and auditable. Clear documentation outlines how to remove accounts, revoke entitlements, and confirm that no orphaned accounts remain. This prevents former employees from retaining access and supports smooth audits. Regularly reviewing and updating the documented policy keeps the deprovisioning process efficient as the organization grows.
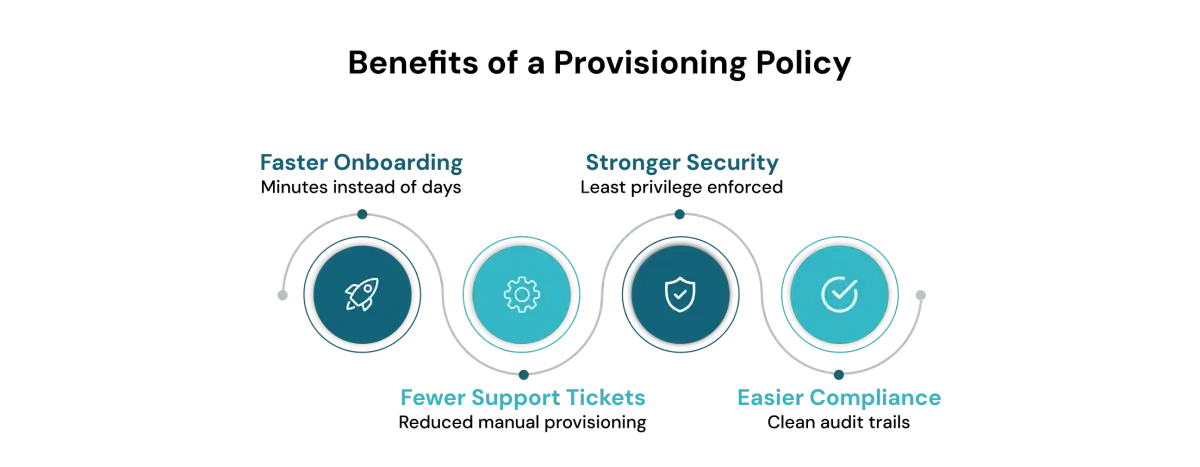
Benefits of Implementing a Provisioning Policy
Automation in user provisioning saves time, reduces errors, and strengthens organizational security.
1. Shorter onboarding time
A well-defined user access provisioning policy ensures that new users receive the correct access as soon as they join. Automated assignment of entitlements, permissions, and service access eliminates manual setup delays and helps employees become productive from day one.
2. Fewer IT support tickets
By standardizing access through predefined role-based rules, organizations reduce the number of support requests related to missing permissions or incorrect access. Automated workflows minimize human error and keep IT teams focused on higher-value tasks instead of repetitive account fixes.
3. Reduced Risk of Data Breaches
A strong user provisioning policy ensures accurate entitlements, enforces the principle of least privilege, and promptly removes or adjusts access as employees change roles or leave the organization. This systematic control of user access minimizes insider threats, unauthorized access, and potential data breaches.
4. Easier audits and reporting
Centralized policy documentation and automated audit trails simplify compliance efforts. Clear records of who received access, when changes were made, and which provisioning policy authorized them help organizations meet regulatory requirements and support faster, more accurate audits.
5. Optimized Costs
Automating access management and lowering the risk of security incidents enables organizations to avoid costly data breaches and regulatory penalties, delivering significant long-term savings.
Best Practices for Policy Design
A well-designed user provisioning policy ensures consistent access, reduces security risks, and keeps identity workflows scalable as the organization grows. When policies follow a clear structure, they remain easier to maintain, audit, and automate across all systems.
Here are the key practices that help keep provisioning policies effective and future-ready.
1. Integrate with HR and IAM Systems
To keep provisioning accurate and up-to-date, link your user provisioning policy with both HR and Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems. Employee lifecycle events such as hiring, promotions, transfers, or exits can then automatically trigger appropriate access changes, eliminating manual delays and reducing the risk of orphaned accounts.
2. Review Access Regularly
Access needs change over time. Conduct regular reviews of all accounts, roles, and privileges to catch outdated permissions or redundant access before they become a security risk. These periodic audits or certifications help maintain compliance with standards and ensure that only current employees have access to sensitive resources.
3. Use Templates for Consistency
Define standard role-based templates or access bundles for common job functions or departments. This ensures that similar roles across the company get the same entitlements and reduces variation due to manual assignment. Templates help simplify onboarding and permissions management, making it easier to provision or revoke access reliably and predictably.
4. Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege
Always grant users only the permissions they need to perform their job. This minimizes risk if credentials are compromised or misused. Combine the principle of least privilege with periodic access reviews and automated deprovisioning to prevent privilege creep and overprovisioning over time.
Example: User Provisioning Policy Template (Editable Framework)
A user provisioning policy provides a structured approach to managing accounts and access throughout the employee lifecycle. It ensures that users receive the correct permissions, security standards are maintained, and access is removed promptly when no longer needed. A clear policy reduces errors, supports compliance, and allows administrators to manage identities efficiently across all systems and applications.
The following framework serves as a template for creating or refining your own provisioning policy.
1. Purpose and Scope
This section defines the objectives of the policy and specifies which systems, applications, and user groups it covers. It explains why the policy exists, whether to govern accounts for a department, an application, or the entire organization, and sets clear boundaries on what resources fall under its control. The scope ensures that all users within the defined area follow the same standards and procedures.
2. Roles and Responsibilities
This section identifies the individuals and teams responsible for implementing and enforcing the policy. Typical roles include IT administrators, HR personnel, security officers, and managers. Responsibilities cover approving access requests, assigning roles, performing periodic reviews, and maintaining documentation. Clearly defining roles ensures accountability and streamlines coordination between departments during onboarding, role changes, or offboarding.
3. Account Lifecycle Rules
Account lifecycle rules describe how user accounts are created, updated, and deactivated. This includes onboarding new employees, modifying access when roles or responsibilities change, and removing accounts promptly when an employee leaves. Automated workflows and predefined rules help prevent orphaned accounts, ensure timely access provisioning, and maintain consistency across all systems. Lifecycle rules also define approval processes for special access requests and temporary entitlements.
4. Security Requirements (MFA, passwords)
This section establishes the security standards every account must meet. Common requirements include multi-factor authentication, password complexity and expiration policies, and authentication methods such as biometrics or smart cards where appropriate. Access controls may also include conditional restrictions based on device, location, or network. Security requirements ensure that sensitive resources are protected and that the organization complies with industry regulations and internal standards.
5. Enforcement and Review
Enforcement and review ensure the policy is effective and followed consistently. This includes regular audits, periodic access reviews, and reconciliation of entitlements with user roles. It also covers how noncompliant accounts are handled, such as revoking unauthorized access or updating misaligned permissions. Documenting all actions and maintaining audit trails provides transparency, supports regulatory compliance, and allows the policy to be updated as the organization evolves.
Final Thoughts
A user provisioning policy is essential for secure, efficient, and compliant identity management. While provisioning ensures that employees get the right access at the right time, it also protects organizations from access sprawl, insider threats, and regulatory gaps.
As businesses scale across hybrid environments and adopt modern identity and access management tools, consistency in how users are onboarded, updated, and deprovisioned becomes critical. Automating access workflows, enforcing least privilege, integrating HR and IAM systems, and maintaining complete audit visibility help IT teams keep every identity accurate, traceable, and secure throughout its lifecycle.
To learn how Tech Prescient supports automated and compliant provisioning aligned with modern identity governance,
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a user provisioning policy?
A user provisioning policy is a formal set of rules that automates how users receive access to systems and data based on their roles or departments. It ensures the right people get the right permissions from day one. This keeps onboarding fast, secure, and fully aligned with compliance standards.2. How do you create a provisioning policy?
To build an effective provisioning policy, you define clear access rules in your IAM or IGA tools. Then you integrate those workflows with HR systems so access gets triggered automatically during hiring, role changes, or exits. Finally, you include automated checks to keep accounts secure and updated.3. What are provisioning rules?
Provisioning rules are the logic sets that map job titles, roles, or departments to the exact systems and permissions a user needs. These rules enforce least privilege by ensuring users only get access relevant to their responsibilities. They also standardize access across teams, preventing inconsistencies.4. What’s the difference between provisioning and deprovisioning?
Provisioning is the process of creating accounts and granting access when someone joins or shifts roles. Deprovisioning removes access instantly when a user leaves or no longer requires systems. Both are critical parts of user lifecycle management in IAM.5. Why is provisioning important in cybersecurity?
Provisioning protects organizations by preventing unnecessary or unauthorized access to sensitive systems. It reinforces least privilege, reduces the risk of data breaches, and keeps identity controls aligned with frameworks like SOX, GDPR, and HIPAA. Good provisioning equals strong security from day one.