User Access Review Process: Step-by-Step Guide, Templates & Best Practices

User access reviews are a fundamental method of discovering and governing who has access to your organization's critical systems and data and of confirming that only the right people have access at the right time, decreasing your risk of internal data breaches.
Imagine this: it's 2019, and a single misconfigured AWS role at Capital One has just created one of the largest financial data breaches ever. A former Amazon employee abused an overly privileged Web Application Firewall role, allowing the individual to access over 100 million customer records.
The aftermath?
- Hundreds of millions in total costs
- Crippling federal penalties
- Sweeping customer settlements
- Potential long-term reputational damage
This incident is just one of many. Organizations all over the world continue to experience data breaches with exploited credentials that allowed overly permissive access, and the financial and reputational aspects of this have an enormous impact.
User Access Reviews (UARs) are just one of the critical defenses against costly data breaches like this. Many organizations are still placing reliance on their bulk, manual processes that are not only time-consuming but are use up valuable resources, when IAM automation tools could streamline these cybersecurity best practices.
Key takeaways:
- Ensures correct access rights are aligned with current job roles
- Supports compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, SOX, and other regulations
- Reduces insider threats and privilege creep by up to 40%
- Should be automated for efficiency - manual reviews are 63% slower
- Delivers measurable ROI through license optimization and risk reduction
What Is the User Access Review Process?
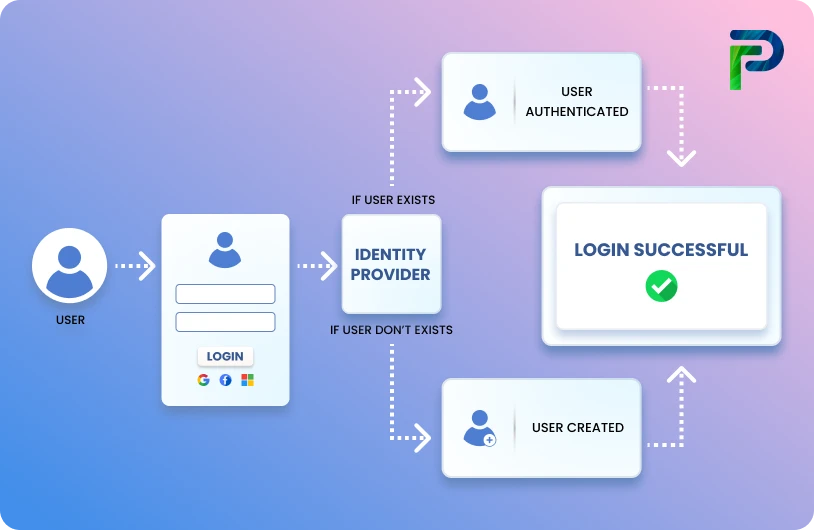
A User Access Review (UAR) is the user access review procedure of validating who has access to your organization's systems, and that access is still warranted. It is the organization's "checkup" to regularly identify and eliminate permissions that are unnecessary or too risky through effective identity governance.
Why User Access Reviews Matter
Every organization encounters the same challenge over time, with employees acquiring access that is no longer needed. Employees may be promoted to new roles and lead contractors that finish projects or vendors that have stopped providing services. The problem is: access is usually retained. These lagging access permissions create security gaps that might cause data breaches or compliance failures, making audit readiness crucial.
How User Access Reviews Work?
The first step in the UAR process is to determine four questions:
- Who is accessing what systems and data?
- What type of access do these users have?
- Why do they need that access in their current role?
- What changes need to be made?
The New UAR Process
Access reviews in today's organization extend beyond employees. The full access review process includes:
- Employees - Full-time, part-time, and temporary employees who need access to perform their job functions
- Business Partners - External organizations that need access to certain systems, limited to their specific assignments
- Vendors - Service providers (i.e., IT support or cloud providers) that need access to support your system or services
- Contractors - Temporary personnel who need access for a specific time to complete work
- Former Employees - The most important category of risk, when a former employee's access is not rescinded
The Process
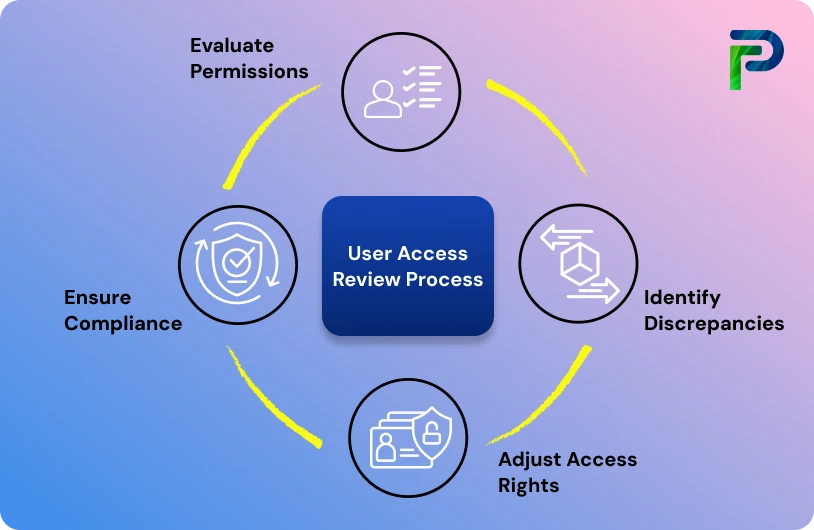
A thorough UAR includes the following steps:
- Define scope - Identify what systems and who the users will be
- Gather data - Get the current permissions from all systems
- Assign reviewers - Managers are best suited since they understand the context of the business
- Validate permissions - Make sure your users have access needed for their job functions
- Take corrective action - Rescind inappropriate or excessive access
- Document actions - Record actions taken for audit purposes Schedule regular reviews - Schedule periodic reviews based on risk
Business Impact
Organizations with a mature user access review procedure had 40% fewer access security incidents than organizations performing annual employee reviews. This illustrates that when you perform access certification regularly, you bolster your security posture while adhering to policies and regulations such as SOX, GDPR, and HIPAA.
Why User Access Reviews Are Critical
User access review is one of the first lines of defense against unauthorized access and security incidents for your organization. User access reviews help to protect sensitive information, adhere to compliance requirements, and mitigate operational risk through proper access control. Organizations that do not conduct user access reviews regularly are exposing themselves to increased security risks and regulatory action that can result in financial consequences and disrupt and damage business operations.
Protecting Sensitive Data
Data breaches can be costly and are increasingly commonplace, with most data breaches accompanied by stolen credentials or misuse by employees, highlighting the importance of cybersecurity best practices.
Consider the Capital One breach as a cautionary tale. One AWS role had far too much access for what they needed, violating the least privilege principle, which resulted in 106 million compromised records and hundreds of millions in losses. If the organization had conducted reviews of all its access rights, it potentially would have caught this excessive privilege before it became an issue.
Healthcare organizations are facing even stricter penalties. The Anthem breach resulted in nearly 79 million records being exposed after a lack of controls around admin accounts led to significant costs and regulatory penalties, emphasizing the need for audit readiness.
Preventing Common Access Issues
There are three common issues that most organizations deal with, namely, employees retaining old access associated with prior roles, orphaned accounts from employees who have left, and spam admin privileges that expand without restraint, all violations of least privilege principles.
Privilege creep occurs naturally within organizations as employees change roles or take on special projects. An employee with many years of service may have access that spans multiple departments, all of which they no longer operate in, requiring periodic user access review procedure to identify these issues.
Orphaned accounts are remnants of former employees or employees who have changed roles. These dormant credentials are appealing to attackers who know they are hard to target. The SolarWinds attack was partly successful due to poorly monitored development accounts, highlighting gaps in identity governance.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Compliance is no longer a luxury. It is now mandatory with real financial implications:
- SOX requires an audit of financial systems quarterly, with significant corporate penalties and potential executive and personal liabilities
- HIPAA requires that you develop and document access procedures for data, and it has very significant fines associated with violations
- GDPR requires regular security testing, with penalties of €20 million or 4% of global revenues
- PCI DSS now requires a semi-annual review of user access, and fines on an ongoing basis for non-compliance
Reducing Licensing Costs
Proper access reviews typically uncover cost savings as well. Companies frequently uncover software licenses assigned to individuals no longer employed by the organization or applications that are no longer in use.
Regular access reviews will identify these inefficiencies, allowing funds to be repurposed or unused licenses canceled. In addition, access reviews reduce administrative overhead by simplifying account and permission control as unnecessary accounts and permissions are identified and removed through effective IAM practices.
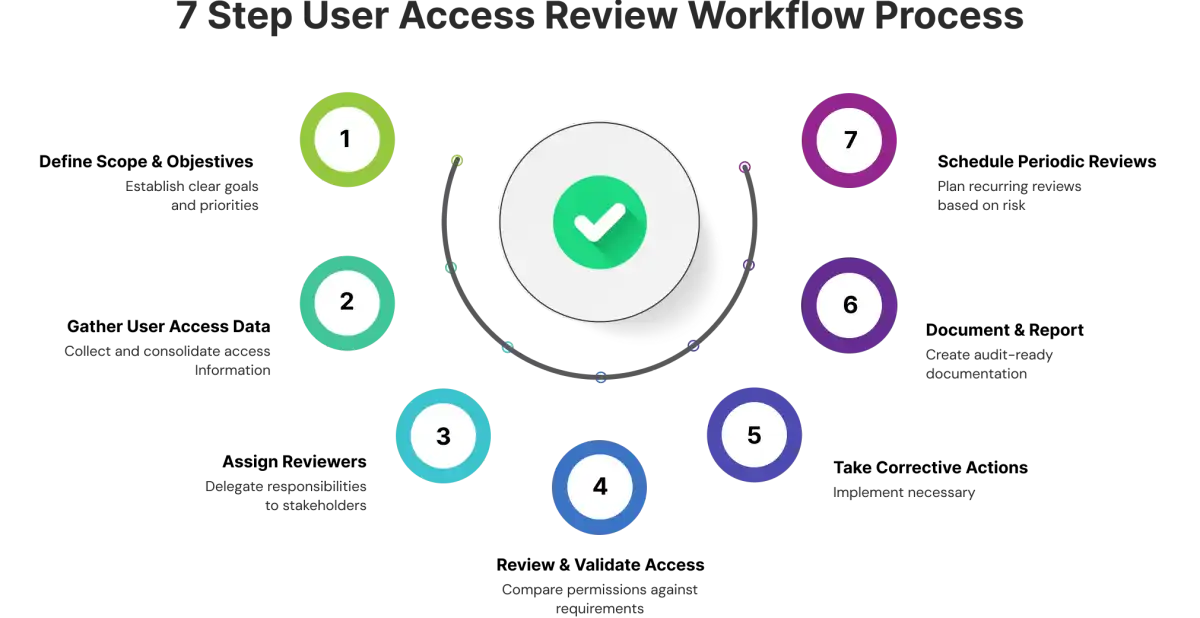
Step-by-Step User Access Review Process
These 7 steps assist you in an effective, compliant access review that mitigates security risk while satisfying regulatory obligations following this comprehensive access review checklist.
Step 1: Scope and Purpose – First, you have to take stock of all the tools and technologies currently existing in your organization. Create a record of all of the users, from internal employees to external partners and contractors, and terminated users, noting what specific access and privileges each one has on each tool and technology. Be sure to identify if they are admins or standard users and indicate all privileged account access. Once you complete the inventory, assess whether or not their access rights are still appropriate/needed for their respective roles, or if any changes need to be made based on their current job functions and security requirements, following the least privilege principle.
Step 2: Populate User Access Data – Export user listings, roles, and permissions from all systems using automated IAM automation tools. Request and extract user access data from all applications, including user name, role, user access level, and last access date. Compile this data into a central location (preferably a secure database or data warehouse) with separate tables and fields for every user, organized by department, role, system, or access level, for ease of access review processing.
Step 3: Leverage Reviewers – Assign user access reviewers by involving business executives, such as system owners and managers, who can weigh the operational requirements of access. When identifying reviewers for each system and application, the typical reviewers will include department heads for business applications, IT security teams for infrastructure access, and system owners for specialized applications. Differentiate roles with clear communication on reviewer responsibilities with stakeholders as part of identity governance.
Phase 4: Review & Validate Access – Compare permissions to job duties using principles of role-based access control and identify unnecessary privileges. Use methodical validation against job descriptions, actual job duties, and identification of unnecessary privileges through the process of least privilege. Validate with HR records for employment and role verification to confirm employment, and validate any discrepancies that require remediation immediately to maintain audit readiness.
Phase 5: Remediation Actions – In accordance with the results of the risk assessment, rights may be removed, changed, or downgraded. Access rights must be revoked immediately from terminated employees, partners, and third-party vendors. In addition, access rights must be verifiably reviewed for current employees for any role limitations and/or access changes that are applicable to their duties. Also, a careful review of excessive rights must be done to ensure that legitimate business functions aren't affected during the process, maintaining cybersecurity best practices.
Phase 6: Documenting & Reporting – Retain records of all review efforts that are audit-ready, including all decisions and remediation actions taken against each user. Compile a comprehensive review report, including the review scope, review methodology, review findings, and the remedial actions that were taken. Maintain standard documents to record review decisions and rationale for each change, such as signed authorization, supporting compliance audit requirements.
Step 7: Schedule the Reviews – Schedule reviews regularly and according to risk levels - quarterly for really high risk systems and annually for lower risk systems as part of your periodic user access review procedure. Use a standardized calendar for the review process that takes into account when the organization conducts operational periods, compliance periods, and considers the capacity of staff to conduct reviews. Include a method to use event-driven review cycles for events such as employees employees leaving the organization, role changes, or security occurrences following your user access review process flow.
During the review, there will need to be controls established to provide evidence of governance principles. These include:
- Approve Authority: Ensure you know who has approved authority to access requests and how you can ensure that all access requests have gone through proper security approvals with designated approvers, depending on access level.
- Evidence of Documentation: Provide compliance with a complete audit trail that outlines who made the request, approval, and subsequently modified access permissions. You will also need details of the timestamps of the action.
- Authentication Controls: Ensure there is evidence of the MFA and authentication controls in place - this is especially pertinent for sensitive accounts that require additional layers of authentication.
User Access Review Process Best Practices
- Successful UAR programmes require strategic implementation that balances thoroughness with efficiency following cybersecurity best practices.
- Be consistent with review frequency by establishing risk-based schedules that align with business operations and regulatory requirements. Privileged accounts and financial systems require quarterly attention, while standard user access may only need annual certification as part of your periodic user access review procedure. Document these schedules clearly and communicate them well in advance to enable proper planning.
- Integrate reviews into employee lifecycle management to ensure access changes align with role transitions, promotions, and departures through effective IAM processes. Implement automated workflows that trigger access reviews when HR systems detect role changes, and establish standard user access review procedures for both onboarding and offboarding that include comprehensive access validation. This integration prevents access debt from accumulating between formal review cycles.
- Enforce the least privilege principle consistently across all access decisions, granting only the minimum permissions necessary for job functions. Train reviewers to understand this principle and provide clear guidelines for evaluating access appropriateness. Regular training ensures reviewers can distinguish between necessary access and convenience access that increases security risk without business benefit, supporting audit readiness.
- Document every change with clear rationale, approval chains, and timestamps to meet audit requirements and support future reviews. Implement standardized templates that capture decision rationale, business justification for exceptions, and approval signatures. This documentation serves dual purposes of satisfying compliance requirements and creating institutional knowledge for future reviews through proper identity governance.
- Leverage automation tools like Tech Prescient’s Identity Confluence to turn manual processes into intelligent automation workflows. This modern IGA platform applies AI to automatically discover high-risk access patterns, converts technical permissions into business-friendly descriptions, and automates low-risk decisions, all to reduce review demands while improving security outcomes via intelligent risk assessment and bounded human decision-making using IAM automation tools
Common Challenges & How to Overcome Them
- Resource-intensive process challenges organizations with limited IT and security staff to complete comprehensive reviews. The manual effort required creates significant demands on already stretched teams.
Solution: Implement automation platforms that eliminate tedious data collection work and provide intelligent risk-based filtering. Start with high-volume, low-complexity reviews to demonstrate quick wins, then expand automation to more complex access decisions. - Complexity in large environments multiplies as organizations manage 500+ applications across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid infrastructures. Inconsistent user naming, limited API availability, and fragmented identity data create visibility gaps.
Solution: Implement a centralized identity governance platform with built-in connectors for the major applications that your organization uses, along with custom integration support for proprietary applications. Organizations can achieve total visibility across 50+ cloud and on-prem applications with advanced platforms that integrate with SCIM, REST APIs, SAML, and OAuth, with the ability to create a unified identity view that removes fragmentation and enables real-time governance and operational capabilities as organizations traverse hybrid environments. - Resistance from stakeholders occurs when business users view access reviews as IT impositions that interrupt productive work without clear value. Department managers may lack context to make informed access decisions or fear that removing access will disrupt operations.
Solution: Provide executive sponsorship demonstrating organizational commitment while educating stakeholders on security benefits. Streamline workflows to minimize business disruption and create feedback loops showing how reviews improve security posture. - Poor documentation practices lead to repeated evaluation of the same access issues and an inability to demonstrate compliance during audits. Many organizations lack standardized templates or fail to capture decision rationale, creating gaps in audit trails.
Solution: Implement standardized documentation templates with immutable logs that retain all review activities, decisions, and timestamps. Deploy systems that produce compliance-ready documentation for on-demand compliance with SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulatory frameworks, with downloadable templates and exportable reports that indicate continuous compliance with audit requirements.
Tools to Automate User Access Reviews
The identity governance market has many solutions available for automating the UAR process, including enterprise platforms with multiple functions and tools that focus on a specific niche. All of the modern IGA platforms can support the automation of user provisioning, provide role-based access controls, and enhance compliance processes.
Some capabilities to consider include:
- Automated user lifecycle management with provisioning in real-time
- Enforcement of role-based access control to mitigate the risk of privilege abuse
- Automation of compliance standards in tandem with regulatory frameworks
- The ability to monitor in real-time while tracking user activity
- Connector integration with existing Identity Providers through API
- Custom reporting capabilities for audit purposes
Engaging with market options can provide enterprise solutions that provide holistic IGA suites, intuitive platforms with many integrations included, or niche or specialized solutions that only address privileged access management.
Supercharge the UAR process with Tech Prescient's Identity Confluence, which presents a cloud-native AI-driven solution that has intelligent capability through automation, without fluffing out configuration requirements, and can be easily integrated with existing infrastructure through API or pre-built connectors as part of comprehensive IAM automation tools.
When looking at the various automation platforms, keep in mind that reviewed capabilities provide value, whether they demonstrate a purpose or demonstrate risk-based review prioritization, as well as useful workflows that provide risk-based review where permission has been obtained. Effective platform, choose a platform that provides the necessary capabilities, but is adaptable for implementation following your user access review process flow. The worst-case scenarios with adoption are choosing a basic platform that needs replacement or a highly engineered platform that is never used.
User Access Review Checklist & Template
A comprehensive UAR checklist ensures consistent, thorough reviews across all systems and review cycles supporting audit readiness. Pre-review preparation checklist includes confirming system inventories remain current, validating reviewer assignments and contact information, establishing clear scope and timelines, preparing necessary reports and data exports, and communicating review initiation to all stakeholders. Complete preparation prevents delays and confusion during active review phases.
User access validation template systematically evaluates each user's access appropriateness:
- Verify current employment status through HR system integration
- Confirm job roles align with assigned permissions
- Validate access against documented role requirements
- Check for segregation of duties violations
- Review privileged and administrative access with enhanced scrutiny
- Identify dormant accounts unused for 90+ days
- Flag access outliers requiring additional investigation
Access modification workflow structures remediation following review findings. Include immediate actions for high-risk findings like terminated employee access, scheduled modifications for role-based adjustments, temporary access grants with automatic expiration, privilege reduction following least-privilege principles, and comprehensive exception documentation with business justification and approval chains supporting compliance audit requirements.
Documentation templates capture essential compliance information, including user identity verification, role-based access matrices, business justification for access requests, approval signatures with timestamps, segregation of duties validation, and final review sign-off. Standardized templates ensure consistent information capture while supporting audit requirements across multiple regulatory frameworks.
Review the cycle calendar template, establish predictable schedules enabling stakeholder planning as part of your periodic user access review procedure. Define quarterly cycles for privileged accounts, semi-annual reviews for regulated systems, annual enterprise-wide reviews during slower business periods, and event-driven triggers for role changes and security incidents following your user access review process flow. Publish calendars well in advance with a minimum three-week notice for reviewers.
Final Thoughts
User access reviews have transitioned from a manual compliance activity to an automated, intelligent security control. Organizations cannot risk lengthy review cycles or whether access governance is just compliance, given the increased costs of breaches and insider threats, making cybersecurity best practices essential.
Identity governance is a strategic security initiative, and not a checkbox activity. The organizations with the most successful identity governance programs integrate direct executive sponsorship, try as much as possible to integrate business into the governance, integrate risk-based automation with human review through IAM automation tools, and create a culture of continual monitoring with periodic user access review procedures. Organizations like this will have fewer security incidents, less review overhead, and save significant costs based on better license management.
Emphasize automation & compliance readiness through platforms like Tech Prescient Identity Confluence that transform UAR from dreaded compliance tasks into strategic security advantages. Intelligent automation reduces complexity while improving effectiveness, enabling organizations to achieve genuine security improvements alongside regulatory compliance following the least privilege principle.
The continued evolution toward zero-trust architectures makes continuous access validation even more critical. Organizations establishing mature UAR programs today position themselves for this transition, building the processes, tools, and culture required for dynamic, risk-based access management through comprehensive identity governance. The question is not whether to implement automated user access reviews, but how quickly organizations can transform their identity governance capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the user access review process?
It's a structured procedure to verify that users have only the access they need for their current job roles. The process systematically examines user permissions across systems and applications, validates access against business requirements, and removes or adjusts inappropriate privileges to maintain security and compliance.2. How often should user access reviews be performed?
Review frequency depends on risk levels and regulatory requirements. Quarterly reviews are recommended for privileged accounts and financial systems, semi-annual for healthcare and regulated industries, and annual for standard user access in low-risk environments. Event-driven reviews should occur for role changes and security incidents.3. What's the difference between a user access review and an audit?
User access reviews are ongoing operational controls that organizations perform regularly to maintain proper access governance. Audits are formal assessments conducted by independent parties to verify compliance with regulations and internal policies. Reviews prevent issues that audits might discover.4. What tools can help automate the process?
Modern Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) platforms like Tech Prescient Identity Confluence, SailPoint, Okta, and Microsoft Entra ID Governance provide automation capabilities. These tools offer risk-based prioritization, automated data collection, intelligent recommendations, and compliance reporting to streamline the review process.5. What is the principle of least privilege in access reviews?
The principle of least privilege means granting users only the minimum access necessary to perform their job functions effectively. During access reviews, this principle guides decisions to remove excessive permissions, downgrade unnecessary privileges, and ensure access aligns with current role requirements rather than accumulated historical permissions.