User Access Review Audit: Process, Steps & Compliance Tips

A user access review audit is similar to a regular security assessment for your business, which ensures that each user in the company has the right amount of access to data and applications. Simply said, a UAR audit, also known as a user access review, is the process of checking and validating user access rights and permissions to make sure that no one has greater access than is necessary. This adheres to the concept of the principle of least privilege and guarantees that the organization remains compliant with critical security requirements and legislation.
Regular user access review audits are an important protection for any firm, as they contribute to the prevention of data breaches and reputational harm. Checking and validating user access privileges on a regular basis improves data security, defensive mechanisms, and demonstrates a strong commitment to fulfilling essential industry compliance standards.
A recent report by Secureframe found that 86% of data breaches happen because of stolen or misused login details. That’s a huge number. One of the best ways to lower this risk is through regular user access reviews, as they make sure employees only have the access they actually need. With that in mind, let’s break down why UAR audits matter, how to run them step by step, and some best practices to keep the whole process simple and compliant.
Key Takeaways:
- What a UAR audit is and its role in enforcing the principle of least privilege
- Why UAR audits are essential for security, compliance, and efficiency
- The main types of user access reviews and their use cases
- Step-by-step process to conduct a successful UAR audit
- Best practices and automation tips to streamline audits
What is a User Access Review Audit?
A user access review audit is a structured, periodic assessment of user permissions and access rights across an organization’s information systems. Its purpose is to confirm that users have only the access required for their job functions, aligning with the principle of least privilege. Through this process, organizations can detect and correct instances of excessive, unauthorized, or inappropriate access. In doing so, they enhance security, reduce the risk of data breaches, prevent issues such as privilege creep, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements like GDPR and SOX.
For example: Imagine a large financial institution handling sensitive data across multiple applications, databases, and systems. To maintain security and compliance, the organization launches a UAR audit aimed at thoroughly reviewing employee access rights and aligning them with regulatory requirements. During this process, IT administrators carefully verify each user’s access, ensuring they have the necessary permissions to perform their duties, nothing more. This minimizes unnecessary privileges, reduces risk, and strengthens the overall security posture. Beyond security, it also supports a robust compliance framework, promoting both efficiency and accountability across the organization.
Why User Access Review Audits are Critical?
With data breaches on the rise, controlling and securing access to sensitive information has never been more crucial. The importance of conducting user access review audits can be highlighted through a few core aspects:
Data Security Assurance
As employees transition between roles, they often retain access privileges that no longer align with their responsibilities. This leftover access increases the organization’s attack surface and exposes it to risks of unauthorized use.
User Access Reviews (UARs) address this by detecting and removing unnecessary permissions, ensuring only the minimum required rights are active. By enforcing the principle of least privilege, UARs reduce opportunities for misuse, exploitation, or accidental exposure of sensitive data.
Mitigation of Insider Threats
Unchecked access often creates conditions for insider risks. UARs help prevent three common scenarios:
- Privilege Creep: The gradual accumulation of excessive permissions as employees change roles without revoking outdated access rights.
- Privilege Abuse: Intentional exploitation of legitimate access for malicious purposes such as data theft, IT system sabotage, or fraud.
- Privilege Misuse: Inappropriate use of legitimate access without malicious intent, such as accessing sensitive data out of curiosity, potentially leading to compliance violations or accidental data leaks.
By addressing these risks systematically, organizations strengthen their security posture and reduce the likelihood of internal threats.
Adaptability to Organizational Changes
Organizations are constantly evolving, employees change roles, departments restructure, and new applications are introduced. Without regular reviews, access rights can quickly become outdated or excessive. UARs ensure that permissions remain aligned with current job functions and organizational needs, maintaining agility without compromising security.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries operate under strict frameworks like GDPR for data protection, HIPAA for healthcare privacy, and SOX for financial reporting. These standards often mandate periodic access reviews to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized use. UARs provide a clear, auditable record of who has access to which systems and when changes occurred, evidence that is invaluable during compliance audits. Neglecting this process can lead to regulatory violations, fines, and reputational damage.
Efficient Resource Utilization
Software and platform costs often scale with the number of users or access levels. When dormant or unnecessary accounts remain active, organizations end up paying more than required. UARs provide visibility into actual software usage, enabling better license management, renegotiation with vendors, and reduced expenses, without disrupting functionality.
Proactive Risk Management
Instead of waiting for access issues to escalate into security incidents or compliance failures, UARs enable a proactive approach. By continuously monitoring and adjusting access rights, organizations identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited, ensuring stronger resilience against evolving threats.
Types of User Access Reviews
Different types of user access reviews exist, each designed to tackle specific challenges, whether it’s managing role changes, keeping an eye on high-risk accounts, or ensuring adherence to compliance mandates.
-
Periodic access reviews
Periodic access reviews are done at set intervals to check if users’ access rights match their current roles and responsibilities. These reviews cover all user accounts in the organization and help spot outdated permissions, like access left behind by former employees or users who changed roles. -
Event-driven access reviews
Event-driven access reviews occur whenever significant changes happen in the organization, like onboarding, offboarding, promotions, or department restructuring. These reviews aim to address immediate access risks that come with such transitions. The main goal is to make sure users whose roles have changed have their permissions updated quickly. They can also be triggered after policy updates or security incidents. -
Continuous access reviews
Continuous access reviews involve real-time monitoring and evaluation of user activities and access rights using automated tools and systems. This approach aligns with the concept of continuous adaptive trust, where user permissions are regularly adjusted based on contextual behavior analysis. Advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and behavioral monitoring play a key role in detecting unusual access patterns and reducing risks as they occur. By adopting different types of user access reviews tailored to your cybersecurity strategy, organizations can effectively minimize the risk of inappropriate access.
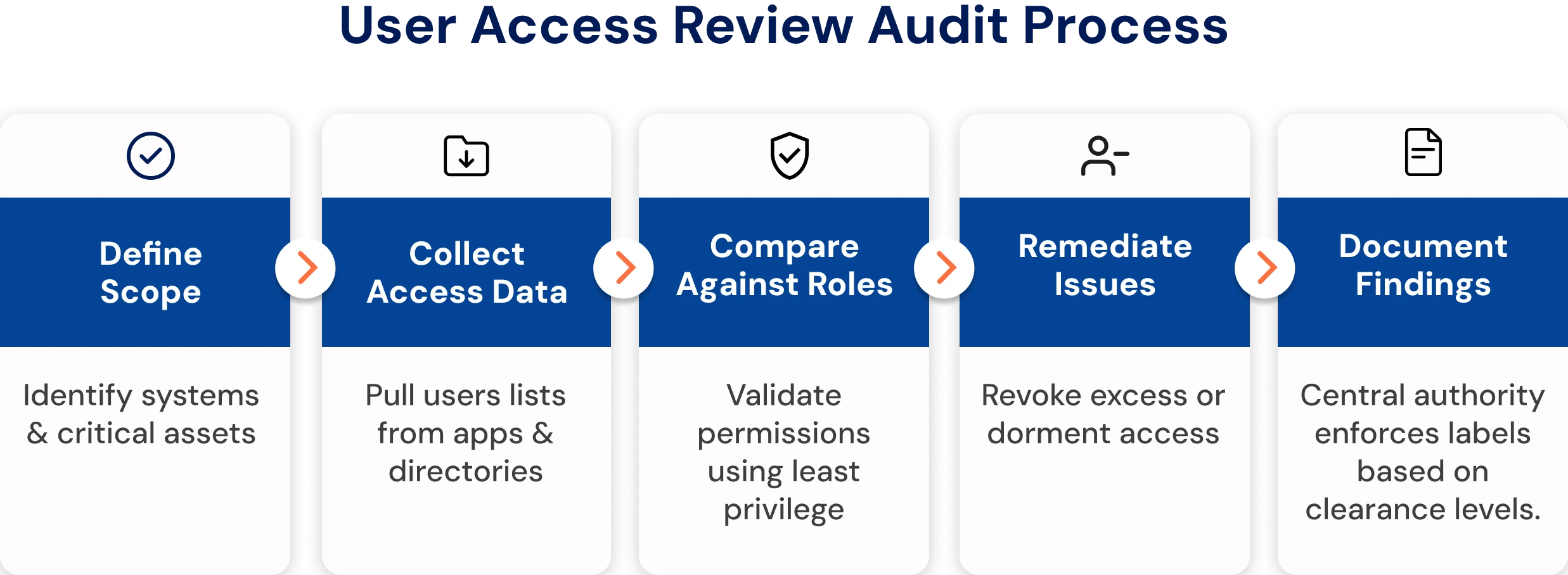
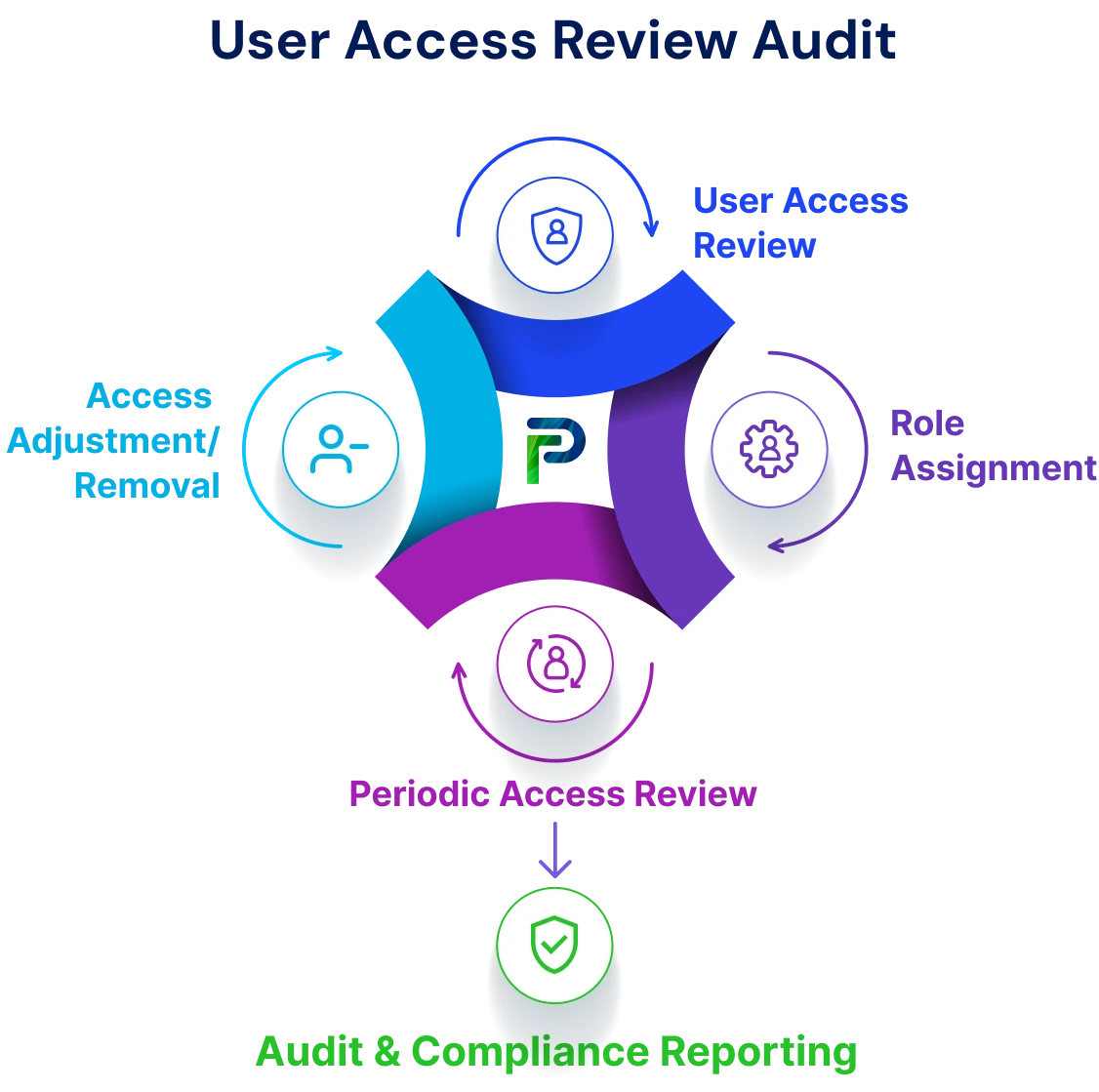
Step-by-Step User Access Review Audit Process
A structured user access review process plays a vital role in reducing cybersecurity risks to your organization’s critical assets. To assist you, we’ve developed a user access review template that can serve as a comprehensive checklist during your audits.
A UAR audit follows five steps: define scope, collect data, compare against roles, remediate issues, and document findings. This ensures access stays compliant and secure.
Step 1. Define the Scope
Start by creating a complete inventory of all systems, applications, and data repositories, covering both on-premises and cloud environments, to ensure no asset is missed. Prioritize these systems based on data sensitivity and potential business impact if compromised. High-risk areas such as financial applications, HR databases, and customer information systems should receive the most attention during the user access review.
Next, identify all relevant regulatory requirements, such as GDPR for EU personal data or HIPAA for PHI in healthcare, to ensure compliance. Include any third-party or vendor systems that have access to your network, as external access points can introduce additional risks and must be part of the review scope.
Step 2. Collect Access Data
Start by compiling a comprehensive list of all organizational assets where sensitive data is stored or processed, including servers, workstations, network devices, cloud services, and databases. For each system, identify how access logs and reports can be generated to track user activity effectively. When extracting access data, you can use automated tools or manual methods:
-
Automated Tools/Scripts: Leverage automation to pull access data, such as usernames, roles, permissions, and last login timestamps, directly from systems. This minimizes manual errors and saves time.
-
Manual Processes: For systems without automation capability, system administrators must manually gather access lists, including user accounts, group memberships, and any special access rights.
Insight: Ensure that every extraction method captures all relevant access control details, from employee IDs and usernames to permission levels (read, write, execute) and exceptions.
Step 3. Compare Against Roles
The Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) ensures that users, systems, applications, and processes have only the minimum access necessary to perform their roles. This minimizes the risk of misuse and limits the impact of potential breaches.
-
User Accounts: Standard users should only have access required for their job functions, while administrative privileges remain strictly limited.
-
Applications and Systems: Assign only essential permissions for applications and processes, preventing unnecessary access to unrelated system areas.
-
Temporary Privileges: When elevated access is needed, grant it on an “as-needed” basis and ensure automatic revocation after the task is complete.
To enforce the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) effectively, review the collected access data to identify and correct privilege excess:
-
Detect Excess Privileges: Look for users with permissions beyond their role requirements, such as access to sensitive data or critical systems unrelated to their responsibilities.
-
Reduce Unnecessary Access: Prioritize adjusting roles, removing users from specific groups, or revoking permissions to align with the least privilege principle.
Step 4. Remediate Issues
Once discrepancies or unauthorized access instances are identified, take immediate corrective measures. Develop a structured process to revoke any outdated, excessive, or unnecessary access rights. Prioritize these actions based on the associated risk level to minimize exposure to potential threats.
Collaborate with the IT security team to ensure revocations are executed without disrupting critical operations. This may involve scheduling changes during non-peak hours or granting temporary supervised access when immediate removal could impact business continuity. Additionally, establish a clear notification protocol for affected users and their managers, outlining the reason for revocation and the correct process for requesting reinstatement if needed.
Step 5. Document Findings
Creating an audit report is critical for maintaining compliance and improving access control processes. This document should provide a complete record of the review, covering the scope, methodologies, findings, and corrective actions taken. It must also clearly document every instance of unauthorized or inappropriate access and the rationale for each corrective step.
Include the following details within the report:
- Scope & Approach: Outline what systems, applications, and data sets were included, and how the review was conducted.
- Issues & Fixes: Document each discrepancy, how it was detected, and the corrective measures implemented.
- Decisions & Challenges: Explain decisions behind access revocations and note any issues encountered during implementation.
Once findings are documented, the report should also define an action plan to prevent similar issues in the future. This plan can include policy improvements, new tools or automation for access reviews, and employee training initiatives. Assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and establish metrics for measuring the effectiveness of these actions.
Best Practices for Effective Access Audits
Conducting effective access reviews demands the right tools and a well-defined strategy. Below are key best practices organizations should follow to ensure a complete and accurate access review process:
Implement (RBAC)
To ensure access rights align with job roles and responsibilities, organizations should adopt Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). This model simplifies access management by assigning permissions to roles rather than individual users. It operates on the principle that access to resources is determined by an individual’s role, which reflects their job function. Key steps to implement RBAC effectively:
-
Define Roles and Permissions: Identify all roles within the organization and determine the set of permissions required for each role to perform its functions.
-
Map Users to Roles: Assign users to appropriate roles based on their job descriptions and responsibilities, ensuring they inherit the correct permissions.
-
Verify Role Alignment: Regularly review job functions against assigned roles to confirm that access remains appropriate and aligned with security policies.
This structured approach reduces complexity, prevents over-provisioning, and ensures that access rights remain consistent with organizational needs.
Automate reviews with IAM/IGA tools
Automation is essential for streamlining user access reviews and ensuring accuracy. Leverage Identity and Access Management (IAM) or Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) solutions that can automate data collection and review workflows. These tools help reduce manual errors and improve compliance. Key considerations when implementing automation:
-
Seamless Integration: Choose tools that integrate with existing systems such as HR applications, Active Directory/LDAP, and cloud platforms to update roles automatically based on HR events like onboarding, promotions, or terminations.
-
Full Lifecycle Management: Ensure the solution supports end-to-end access governance, including user provisioning, periodic reviews, modifications, and detailed documentation.
-
Scalability: Opt for platforms that can scale with organizational growth and manage complex access structures across multiple systems and environments.
Automating reviews with IAM/IGA tools becomes far more impactful with Tech Prescient’s expertise, delivering not just efficiency gains but also enhanced security through real-time alignment of user roles and access rights.
Involve multiple stakeholders
Include department heads and line managers in the access review process to validate whether each user’s permissions are truly necessary. These stakeholders have a clear understanding of operational requirements and can accurately determine the level of access needed for each role.
Their participation helps enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring employees only have access to what is essential to their job functions. This collaborative approach minimizes the risk of over-privileged accounts and strengthens the overall security posture.
Regularly audit logs
In addition to having an access management policy, it’s essential to maintain an updated procedure for reviewing user rights within your organization. Regular reviews ensure that permissions remain appropriate and aligned with the principle of least privilege. If you already have a process in place, evaluate it regularly to confirm its effectiveness and compliance with security requirements.
For teams that still manage certification campaigns manually, adopting Pre-Built Review Templates can significantly streamline the process. These templates provide a standardized framework, ensuring reviews are conducted thoroughly and consistently, regardless of who is responsible. They can also be customized to fit specific user roles, systems, or regulatory requirements, making them a flexible yet reliable tool for enhancing access review procedures.
If you don’t yet have a formalized procedure, create one that clearly defines how and when reviews will occur, who will be responsible for conducting them, and how results will be documented and reported. This should also include timelines for notifying employees about upcoming reviews and establishing the contents of review reports. Having a documented procedure ensures consistency, helps enforce accountability, and strengthens overall access control governance.
Automating User Access Review Audits
Manual user access reviews are often time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale across multiple systems. Automation helps organizations streamline the entire audit process by pulling real-time access data directly from applications, directories, and cloud platforms.
This reduces the risk of human oversight, ensures consistent application of the principle of least privilege, and accelerates review cycles. Instead of relying on spreadsheets and manual sign-offs, automated workflows deliver clear visibility into who has access to what, and whether those entitlements are still justified.
Modern Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) or Identity and Access Management (IAM) platforms take this efficiency a step further. By integrating with core business systems, these tools can automatically flag policy violations, notify managers for approvals, and even trigger remediation actions such as revoking unused accounts or excessive permissions. Leading tools like Okta not only support compliance with frameworks like SOX, HIPAA, and GDPR but also provide auditable logs and structured reports that simplify regulatory submissions. The result is faster reviews, stronger security posture, and reduced operational burden for IT and compliance teams.
User Access Review Audit Report & Templates
A well-structured audit report is essential to prove compliance and demonstrate that user access is being monitored effectively. These reports capture the entire review lifecycle, from accessing data collected, risks identified, and corrective actions taken, to final sign-offs by managers. Clear documentation not only satisfies regulatory requirements (SOX, HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001) but also provides executives and auditors with transparent visibility into how access rights are managed. Without this documentation, organizations risk failed audits, penalties, or blind spots that could be exploited by insider threats.
To make reporting consistent and less time-consuming, many organizations use standardized templates in formats like PDF or Excel. These templates ensure that every review captures the same key details, systems reviewed, users evaluated, access changes made, and compliance status. They also serve as ready evidence during external audits and internal governance checks.
Final Thoughts
User Access Review (UAR) audits are no longer just a compliance checkbox; they are a strategic necessity for safeguarding sensitive data, minimizing insider threats, and ensuring operational efficiency. By embedding structured, recurring reviews into your governance framework, you create a stronger culture of accountability, transparency, and security across the organization.
At Tech Prescient, we help enterprises modernize and automate their user access review processes to reduce risk and stay audit-ready. From aligning with regulatory standards like SOX, HIPAA, and GDPR to leveraging automation with tools such as Okta, our team ensures that the right people always have the right access at the right time.
Don’t wait for an audit finding or a security incident to highlight gaps in your access governance. Take the next step with Tech Prescient today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the objective of a user access review audit?
The main goal is to confirm that every user only has the permissions they need for their current role, nothing more, nothing less. This helps maintain the principle of least privilege and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.2. How often should user access reviews be conducted?
Annual reviews are the bare minimum, but for organizations handling sensitive data, quarterly reviews are a best practice. The more frequent the review, the quicker you can catch and fix access creep.3. What should be included in a user access review audit report?
Your report should clearly outline the scope of the audit, the findings, and any remediation actions taken. Don’t forget compliance sign-offs, they prove the process was completed and meets regulatory standards.4. Can user access reviews be automated?
Absolutely. IAM or IGA tools can automate data collection, streamline reviews, and even flag anomalies. Automation not only saves time but also reduces the risk of human error during the process.5. What are the risks of skipping user access reviews?
Ignoring these reviews opens the door to insider threats, compliance violations, and costly data breaches. It’s like leaving your office doors unlocked, you may not notice a problem until it’s too late.