Segregation of Duties: The Ultimate Guide to Implementation, Examples, and Compliance

What is Segregation of Duties?
Segregation of Duties (SoD) is an important internal control mechanism that is used in various companies to minimize the risk of any kind of fraud, errors, or unauthorized access by ensuring that no single individual is responsible for all aspects of a critical process. This means that responsibilities are split among different individuals to establish checks and balances in daily operations.
Overall, SoD involves dividing tasks related to authorization, custody, record-keeping, and reconciliation. This control is applicable in accounting, cybersecurity, & auditing functions in order to ensure regulatory compliance with standards like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Say For example, one employee may be responsible for approving any payment, another for processing it, and a third for reconciling the accounts afterward.
Why is Segregation of Duties Important?
Implementing SoD plays a crucial role in safeguarding the integrity and efficiency of an organization. Here’s why it is important:
- Fraud Prevention: By dividing or separating the responsibilities, SoD reduces the probability that one person might manipulate a system for their personal gains.
- Error Detection: Multiple individuals involved in a process create natural checkpoints that make it easier to catch mistakes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many frameworks, including SOX and HIPAA, mandate SoD as a mandatory and required control.
- Operational Efficiency: Assigning distinct roles ensures better process management and accountability.
Failure to implement effective SoD can lead to serious risks such as financial fraud, data breaches, reputational damage, and non-compliance penalties.
Segregation of Duties vs. Separation of Duties
Although both of these terms are often used interchangeably, but Segregation of Duties and Separation of Duties have varying distinct contexts.
| Feature | Segregation of Duties (SoD) | Separation of Duties |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Divides tasks across roles for fraud prevention | Splits access/control in IT/security systems |
| Primary Use | Finance, auditing, compliance | Cybersecurity, IAM |
| Example | Separate roles for approving and processing pay | One team provisions users; another audits |
Core Components of Segregation of Duties
Let us now have a look at the four major functions that form the foundation of SoD:
- Authorization
Authorization is the process of granting approval for specific actions and transactions. Only an authorized personnel can give the approval for activities like payments or contract signings, ensuring that all transactions are legitimate and policy-compliant. - Custody
Custody is a process that involves the responsibility of managing assets or even holding them, whether they are physical (such as cash or inventory) or digital (like: data or credentials). An individual with custody although safeguards these assets but they do not have the authority to approve their use or movement. - Record-Keeping
Record-keeping primarily means accurately documenting all transactions and maintaining up-to-date records. Any individual in this role keep a log of and also tracks activities but does not have access to the assets themselves. Neither do they have the authority to approve any type of transactions this ensures transparency and accountability. - Reconciliation
Reconciliation is the independent review and comparison of records with actual assets or external data. This is a crucial aspect as this step checks that recorded transactions matching with reality, helping to identify errors or fraud if any. The person reconciling should not be involved in authorization, custody, or record-keeping.
Example:
Let us understand the above concepts with the help of an example: In a payroll process, an employee enters work hours (that is record-keeping), another individual approves them (authorization), a third person may disburse payments (custody), and a fourth checks the records against bank statements (reconciliation). This separation of duties reduces the risk of mistakes or any kind of fraud.
Segregation of Duties in Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, SoD is crucial for preventing unauthorized access and mitigating insider threats. By dividing administrative tasks, organizations can ensure that sensitive systems and data are not exposed to misuse.
For instance:
- One team may be responsible for provisioning user accounts.
- Another team reviews access logs.
- A third team handles compliance assessments and audits.
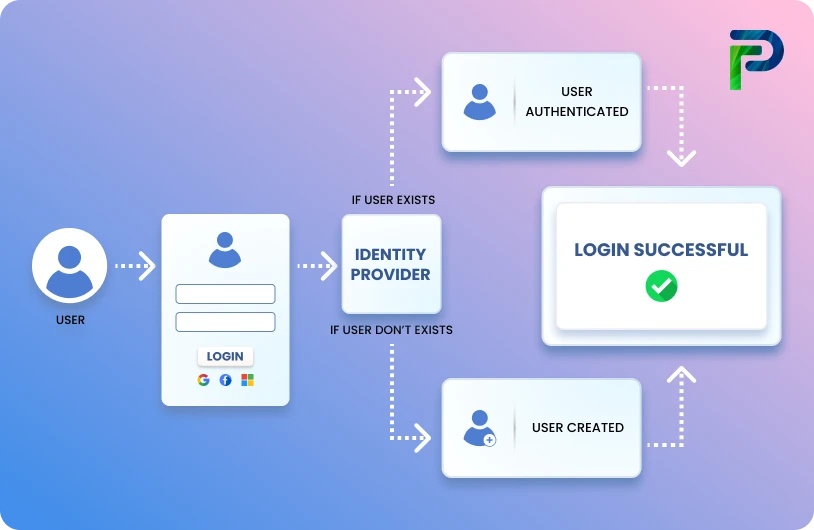
To enforce SoD in cybersecurity, organizations often use Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools these tools automate the distribution and monitoring of access privileges.
Implementing SoD in IT also supports compliance with data privacy and protection regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Segregation of Duties Examples
Understanding how SoD applies to real-world business functions helps clarify its importance. Below are a few examples:
Payroll Process:
- Employee A inputs work hours.
- Employee B approves the timesheets.
- Employee C processes payroll.
- Employee D reconciles payroll reports.
Procurement Process:
- Employee A creates the purchase request.
- Employee B approves the request.
- Employee C receives the goods.
- Employee D issues the payment.
Inventory Management:
- Employee A manages inventory levels.
- Employee B logs the stock movements.
- Employee C conducts periodic stock audits.
These examples show how task division prevents any one person from having total control.
Segregation of Duties in Auditing
Auditors rely heavily on SoD in order to ensure that organizations have strong internal controls and minimal risk to exposure. SoD enhances transparency and objectivity in financial and operational processes.
Audit practices include:
- Reviewing role assignments and permissions.
- Identifying conflicts in user access or workflow.
- Recommending corrective measures to mitigate risk.
Segregation of Duties is also a crucial element in SOX audits, which require companies to prove that financial activities are not controlled by a single individual without oversight.
How to Create a Segregation of Duties Matrix
An SoD matrix is a visual tool that helps organizations identify and manage conflicts in roles and responsibilities. Here's how you can build one:
-
Identify critical business processes such as payroll or procurement.
-
Define the roles involved in each process (e.g., accountant, manager, auditor).
-
Map each role against specific tasks like preparing, approving, or reconciling.
-
Look for overlaps that indicate potential conflicts.
-
Resolve conflicts by reassigning tasks or automating controls.
Example Matrix:
Role | Prepare | Approve | Reconcile |
|---|---|---|---|
Accountant | ✔ | ||
Manager | ✔ | ||
Auditor | ✔ |
This matrix helps visualize how tasks are distributed to ensure adequate control.
Segregation of Duties Checklist
Use the following checklist to ensure your SoD framework is effective:
-
Identify and document critical processes.
-
Map roles and assign responsibilities.
-
Prevent conflicting duties through proper access controls.
-
Deploy IAM tools to manage access and monitor activity.
-
Schedule regular reviews and audits.
-
Provide training on SoD policies and their importance.
-
Automate repetitive or high-risk tasks where possible.
A robust checklist ensures continuous compliance and risk mitigation.
Best Practices for Segregation of Duties Implementation
Implementing SoD successfully requires a blend of people, processes, and technology. Follow these best practices:
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities across departments. The foundation of effective SoD has to be communicated organization-wide. This can be done by ensuring that every employee knows their specific duties and how they align with broader processes. Job descriptions should explicitly outline tasks and limitations of authority to avoid overlap.
- Automate access controls and approval workflows using IGA solutions: Manual processes can lead to errors or overlooked conflicts. Implementing IAM and IGA tools allows organizations to automatically enforce policies, flag violations, and restrict access based on predefined roles. Automation not only increases accuracy but also enhances scalability.
- Conduct periodic internal audits to validate SoD policies. Regular audits help ensure that existing SoD frameworks remain effective as teams evolve and processes change. Audits should examine user access rights, identify conflicting roles, and verify whether controls are functioning as intended.
- Train employees on their specific duties and the importance of compliance. Awareness and education are crucial. Provide mandatory training sessions for all new employees and conduct refresher courses periodically to reinforce the importance of maintaining SoD and avoiding conflicts of interest.
- Maintain proper documentation to demonstrate audit readiness. Documentation is essential for internal governance and external compliance. Keep records of role assignments, access control reviews, training logs, and audit findings. Proper documentation not only improves operational clarity but also simplifies regulatory reporting.
By following these best practices, organizations can establish a robust and sustainable SoD framework that mitigates risk, supports compliance, and fosters a culture of accountability.
Conclusion
Segregation of Duties is not just a best practice—it's a foundational principle for securing your organization's operations, finances, and systems. From reducing the risk of fraud and human error to ensuring regulatory compliance and building a culture of accountability, SoD delivers significant value across industries.
At Tech Prescient, we help enterprises embed these principles through scalable and intelligent Identity Governance solutions. Our platform empowers organizations to automate role assignments, enforce SoD policies, and continuously monitor access controls, all while staying compliant with standards like SOX, GDPR, and HIPAA.
Whether you're just starting to formalize your SoD policies or looking to optimize your existing controls, Tech Prescient offers the tools and expertise to guide your journey.
Secure roles. Minimize risk. Stay compliant with Tech Prescient.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is segregation of duties?
A: It’s a risk management control that distributes responsibilities across multiple roles to reduce fraud and errors.Q: Why is segregation of duties important?
A: It prevents fraud, ensures compliance with regulations, and promotes accountability and transparency.Q: Can you give examples of SoD?
A: Yes. For example, in payroll, different employees handle timesheet entry, approval, processing, and reconciliation.Q: What are the core functions of SoD?
A: Authorization, Custody, Record-keeping, and Reconciliation.Q: How does SoD apply in cybersecurity?
A: SoD separates responsibilities like provisioning, logging, and auditing to avoid conflict of interest.Q: How do I create a SoD matrix?
A: List your roles and tasks, identify overlaps, and mitigate risks using reassignment or automation tools.