IAM Risk Assessment: Process, Risks, and Best Practices


Identity and access management risk assessment is basically a way to check how secure your IAM system really is. Think of it as testing how well your company’s digital assets are protected. The process looks for weak spots in access controls, policies, or user permissions, any gaps that cyber threats could slip through, so you can fix them before they turn into real problems.
IAM risk management is one of the best ways to stay ahead of evolving threats, and it should be a regular part of your company’s security playbook. It secures your digital assets and keeps customer data protected. Thus, helping with compliance and making it easier to attract new clients and secure more business opportunities.
According to research by Augusta University, the cost per data breach in 2023 was around $5 million. Taking preventative measures, such as doing IAM evaluations, is crucial because that is a significant investment. Being HIPAA or GDPR compliant shows strong security and builds client trust. Regularly reviewing and updating your IAM practices keeps your company credible and more attractive to partners.
Let’s explore the blog to uncover more: from the core benefits of IAM risk assessments to actionable insights on how they strengthen your security strategy.
Key Takeaways:
- Learn what IAM risk assessment is and why it’s critical for security and compliance
- Know about common IAM risks, from excess privileges to third-party access issues
- Follow a clear step-by-step approach to spot, prioritize, and fix IAM risks effectively
- See how to use best practices like MFA, least privilege, automation, and regular access reviews
- Discover how conducting IAM risk assessments can improve security, compliance, efficiency, and make things easier for users
What is IAM Risk Assessment?
An IAM assessment examines the effectiveness of access control and authorization processes, taking into account governance, security, and identity management components. Its purpose is to identify gaps or weaknesses within the current framework and provide a clear roadmap for strengthening IAM practices moving forward.
These assessments are critical in mitigating persistent data security threats. Many data breaches stem from credential compromise or unauthorized access, and poorly defined access management policies create exploitable vulnerabilities for attackers.
To prevent such risks, regular or periodic IAM assessments are essential. They help ensure that security controls remain robust, potential threats are addressed proactively, and IAM systems stay aligned with evolving cybersecurity challenges.
Choosing the right identity and access management risk assessment is a vital step in strengthening your company’s security. The assessment you choose should align with your organization’s specific needs, and there are several factors to keep in mind:
- Compliance requirements: Every industry comes with its own regulations (like HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI DSS). Your IAM risk assessment should be tailored to meet those standards, ensuring both data protection and customer trust.
- Internal security expertise: If your team lacks deep cybersecurity experience, look for an assessment that offers built-in guidance. Alternatively, consider tapping into a virtual CISO service for on-demand expertise.
- Budget considerations: While low-cost or free solutions may seem appealing, they often fall short in depth and leave gaps that can create long-term risks. Think of IAM as an investment in resilience.
- Long-term security goals: A good IAM risk assessment doesn’t just patch today’s vulnerabilities. It should also support your future security roadmap and evolving digital environment.
By weighing these factors, you’ll ensure your IAM risk assessment isn’t just a one-time exercise but a strategic tool for building stronger defenses over time.
Common IAM Risks to Watch For
Identity and access management risks aren’t always driven by highly advanced cyberattacks. In many cases, they originate from overlooked basics, like mismanaged permissions or poorly secured credentials. When these gaps go unaddressed, they can quickly evolve into critical vulnerabilities. Here are some of the most common challenges organizations run into:
Excessive Privileges
One of the most common IAM risks comes from granting users or applications more access rights than they actually need. This “permission creep” often occurs when employees change roles but retain old access, or when automation scripts are configured with overly broad permissions. The danger is clear: if an attacker compromises such an account, those unnecessary privileges can be weaponized to move laterally across systems and reach sensitive data. Regularly reviewing and enforcing the principle of least privilege is key to reducing this risk.
Orphaned & Dormant Accounts
Orphaned or dormant accounts, those belonging to former employees, inactive systems, or unused applications, pose a hidden IAM risk. Even though they may no longer be actively used, these accounts often retain access privileges, creating an easy target for attackers. If left unchecked, they can serve as a backdoor into critical systems, allowing unauthorized access or data breaches. Regularly identifying and deactivating unused accounts is essential to maintaining a secure IAM environment.
Weak Authentication Practices
Weak or poorly managed authentication remains one of the most frequent IAM vulnerabilities. Simple passwords, reused across multiple accounts or shared among users, can be easily exploited by attackers. Such practices leave systems open to credential-stuffing attacks, brute-force attempts, and unauthorized access. The risk increases when credentials aren’t stored securely or when multi-factor authentication (MFA) isn’t enforced. Strengthening authentication practices, through strong, unique passwords, MFA, and secure credential storage, is essential to safeguarding critical systems and sensitive data.
Compliance Gaps
Compliance gaps arise when IAM policies and practices fail to meet regulatory or industry standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. These gaps not only increase the risk of security incidents but can also lead to hefty fines and reputational damage. Common issues include incomplete access reviews, lack of proper audit trails, and failure to enforce role-based permissions consistently. Regular IAM assessments help identify and close these gaps, ensuring both regulatory compliance and a stronger overall security posture.
Shadow IT & Third-Party Risks
Shadow IT occurs when employees use apps or software that haven’t been approved or managed by the IT team, often to make work faster or easier. These tools may improve productivity but often lack proper security controls, leaving sensitive data exposed and creating blind spots for IT teams. Similarly, third-party vendors, contractors, or partners frequently require access to internal systems. If this external access isn’t properly managed, monitored, and de-provisioned when no longer needed, it can become a critical vulnerability. Maintaining strict visibility, enforcing access policies, and regularly auditing third-party permissions are essential steps to mitigate these risks.
Analyze User Activity
Monitoring user activity is crucial for detecting suspicious or unauthorized behavior before it escalates into a security incident. Unusual patterns, such as logins from unexpected locations, access to sensitive data outside normal working hours, or large-scale file downloads, can indicate compromised accounts or insider threats. Implementing continuous user activity monitoring and leveraging analytics helps organizations quickly identify anomalies and respond proactively to potential risks.
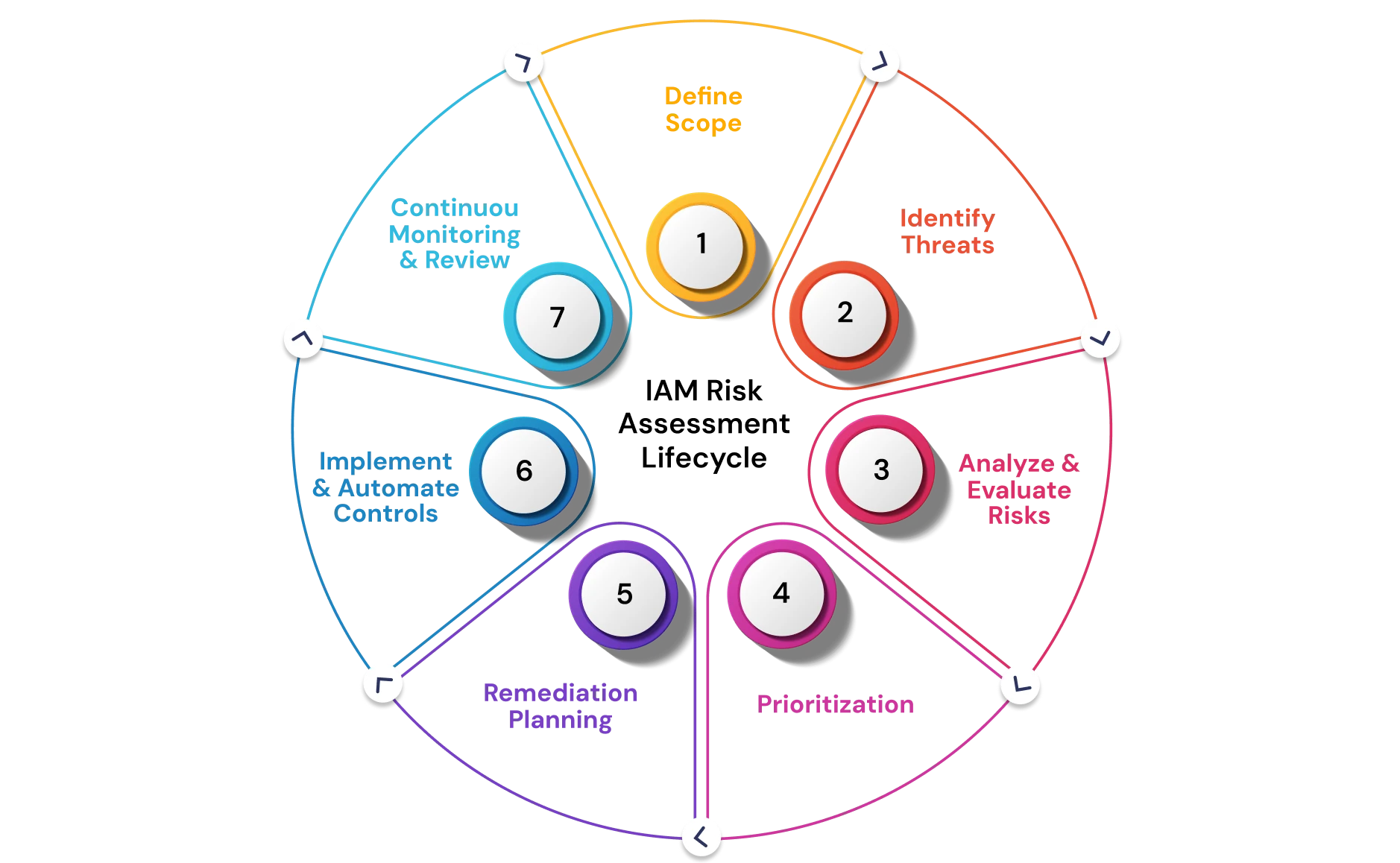
Steps in an IAM Risk Assessment
A comprehensive IAM risk assessment follows a structured process designed to identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities across your organization’s identity and access management environment.
Step 1. Define Scope
The first step in an IAM risk assessment is to clearly define its scope and objectives. Start by identifying the organization’s critical assets, such as key systems, applications, and sensitive data, that must be protected. This also involves determining which users have access to which resources or applications, ensuring that access aligns with their roles and responsibilities. Next, outline the goals of the assessment, whether it’s to uncover vulnerabilities, ensure regulatory compliance, or strengthen the overall security posture.
Finally, set clear boundaries for the assessment by deciding which departments, user groups, systems, and processes will be reviewed. Having a well-defined scope makes sure the assessment stays focused, delivers actionable results, and aligns with the organization’s overall security priorities.
Step 2. Identify Threats & Vulnerabilities
The next step in an IAM risk assessment is to pinpoint potential threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise your organization’s security. This includes detecting access violations, where users gain unauthorized access or deviate from established access policies. It also involves identifying excessive privileges, such as accounts with permissions beyond what is required for their roles, which can be exploited if compromised.
Dormant or inactive accounts must be flagged, as they can serve as hidden entry points for attackers. Additionally, compliance gaps should be assessed to ensure that IAM practices meet relevant regulatory standards and industry requirements. By thoroughly identifying these risks, organizations can gain a clear understanding of where their IAM system may be exposed and prioritize areas that require immediate attention.
Step 3. Analyze & Evaluate Risks
Once threats and vulnerabilities have been identified, the next step is to analyze and evaluate their potential impact. This involves categorizing each risk based on its severity, whether high, medium, or low, and understanding the possible consequences for your systems, data, and overall security posture. It’s also important to identify which applications, systems, or resources require the highest level of protection, as this helps in aligning security measures with business priorities.
Additionally, performing a root cause analysis helps uncover the underlying factors that led to each vulnerability, such as misconfigured permissions, weak authentication practices, or gaps in policy enforcement. By thoroughly analyzing and evaluating risks, organizations can prioritize remediation efforts effectively and address the most critical vulnerabilities first, ensuring a stronger and more resilient IAM framework.
Step 4. Prioritize Risks
After analyzing and evaluating risks, the next step is to prioritize them based on their severity and potential impact. Categorizing risks as high, medium, or low helps organizations focus their remediation efforts on the vulnerabilities that pose the greatest threat to critical systems, sensitive data, and overall security posture.
High-risk issues, such as accounts with excessive privileges or active compliance gaps, should be addressed immediately, while medium and low risks can be scheduled for remediation based on available resources and operational priorities. This structured approach ensures that time and effort are spent effectively, strengthening the IAM framework while minimizing potential business disruption.
Step 5. Remediation Planning
Once risks are analyzed and prioritized, the next step is to implement remediation strategies to strengthen security and reduce vulnerabilities. Key measures include:
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Access: Instead of granting permanent elevated permissions, assign access temporarily based on specific tasks or user behavior, with automatic revocation when no longer needed.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add extra layers of verification to ensure only authorized users can access critical systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized access from stolen or weak credentials.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions according to user roles rather than individuals, enforcing the principle of least privilege and simplifying access management.
Implementing these strategies ensures that access is tightly controlled, vulnerabilities are addressed proactively, and sensitive systems and data remain protected.
Step 6. Implement & Automate Controls
After planning remediation strategies, the next step is to implement and automate IAM controls to ensure consistent enforcement and continuous protection. Leveraging IAM platforms with automated, real-time assessment capabilities allows organizations to identify vulnerabilities as they arise, rather than waiting for periodic manual audits. Automation can streamline access provisioning and de-provisioning, enforce policies consistently, and provide alerts for unusual activity or policy violations. By integrating automated controls, organizations reduce the risk of human error, maintain tighter security over critical systems and data, and ensure that their IAM processes remain effective and up to date.
Step 7. Continuous Monitoring & Review
The final step in an IAM risk assessment is to establish ongoing monitoring and periodic reviews to ensure sustained security and compliance. Continuous monitoring involves tracking user activity, access patterns, and system behavior in real time to detect and respond to anomalies or potential threats quickly.
Complementing this, periodic reviews of IAM policies, access rights, and control mechanisms help verify that they remain effective, up to date, and aligned with organizational goals and regulatory requirements. By combining real-time monitoring with regular audits, organizations can maintain a proactive security posture, quickly address emerging risks, and ensure their identity and access management framework continues to protect critical systems and data effectively.
Get Expert Support
Next, assess your internal security expertise before proceeding. If your team lacks deep cybersecurity experience, choose an assessment that offers comprehensive guidance and hands-on support. And if that still doesn’t meet your needs, consider leveraging platforms like Tech Prescient’s Identity Confluence, which provides the expertise and advanced tools you need to strengthen your IAM framework and move in the right direction with confidence.
Best Practices for IAM Risk Management
Adopting effective IAM best practices is crucial to reducing security risks, maintaining compliance, and protecting critical systems and data. The following measures help organizations build a resilient IAM framework:
- Enforce MFA Across All Accounts
Implement multi-factor authentication for every account, especially for users with elevated privileges. MFA adds an extra layer of verification, making it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Regularly review and update MFA settings to ensure they cover all potential access points. - Apply the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
Limit user access to only what is necessary for their roles. This minimizes the risk of accidental or malicious misuse of privileges and reduces the attack surface. Periodically audit permissions to ensure they remain aligned with current responsibilities. - Automate User Provisioning & De-Provisioning
Use automated tools to manage onboarding, role changes, and offboarding. This ensures accounts are created and removed promptly, reducing the risk posed by orphaned or inactive accounts. Automation also enforces consistency and prevents manual errors. - Conduct Regular Access Reviews
Schedule frequent audits to verify that user access aligns with business roles and responsibilities. These reviews help detect over-privileged accounts, dormant users, and policy violations. Corrective actions can then be taken proactively to maintain security. - Integrate IAM with Compliance Frameworks
Align IAM policies with regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO standards. Integration ensures that access management practices meet compliance obligations and are auditable. This also reduces the risk of penalties and enhances trust with stakeholders. - Use Anomaly Detection & Logging
Continuously monitor user activity and system behavior to detect unusual patterns that could indicate a security breach. Maintain detailed logs of all access events to enable forensic analysis and incident response. AI-driven monitoring can enhance detection and reduce response times.

Benefits of Conducting IAM Risk Assessments
Conducting regular IAM risk assessments delivers valuable insights that strengthen security, streamline operations, and enhance compliance across the organization. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Security Posture
Risk assessments help identify vulnerabilities, over-privileged accounts, and weak access controls before attackers can exploit them. This proactive approach strengthens the overall security posture. By addressing gaps promptly, organizations can protect sensitive systems and data more effectively. - Compliance Readiness
Regular assessments ensure that IAM practices align with regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX. Maintaining compliance reduces the risk of penalties and audits. It also demonstrates to stakeholders that security policies are robust and well-managed. - Data Protection:
An IAM audit reviews how well your organization safeguards sensitive data. It involves analyzing who has access to critical information and verifying whether those access rights are properly assigned and aligned with security policies. - Reduced Costs from Breach Prevention
By identifying high-risk accounts and potential vulnerabilities early, organizations can prevent costly security incidents. Investing in proactive IAM assessments reduces the financial and operational impact of breaches. This approach also avoids expenses related to emergency remediation and regulatory fines. - Incident Response:
A thoroughly audited IAM system plays a critical role during a security incident. It allows IT teams to quickly detect compromised accounts, revoke access, and contain the breach, minimizing its overall impact and reducing potential damage. - Improved Operational Efficiency
IAM risk assessments uncover redundant or misaligned access rights, helping organizations streamline user provisioning and de-provisioning. Optimizing access management processes reduces administrative overhead and prevents errors. Teams can operate more efficiently while maintaining secure access controls. - Better User Experience with Right-Sized Access
Assessments ensure that employees and systems receive access aligned with their roles and responsibilities. This reduces frustration from unnecessary restrictions while maintaining security. Providing the right level of access enhances productivity and supports a smoother workflow across the organization.
Final Thoughts
IAM risk assessments are essential to keeping your business secure, compliant, and audit-ready. By making them a regular part of your governance framework, you not only prevent breaches but also build trust with customers and regulators.
At Tech Prescient, we help enterprises modernize IAM, automating assessments, enforcing least privilege, and ensuring compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
Get ready to strengthen your IAM strategy with Tech Prescient today and secure your enterprise.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the 4 pillars of IAM?
The four pillars of IAM form the foundation of secure access management. Authentication ensures the right user is verified, Authorization gives them only the access they need, Administration handles adding or removing accounts, and Audit & Compliance makes sure everything aligns with policies and regulations. Together, these pillars keep access both seamless and secure.2. How often should IAM risk assessments be performed?
Ideally, IAM risk assessments should happen at least once a year. However, if your organization is in a highly regulated industry or is going through big changes like mergers, new technology rollouts, or system upgrades, more frequent reviews are crucial. Regular assessments reduce gaps and help you stay compliant.3. What are the common IAM risks organizations face?
Some of the biggest IAM risks include excessive privileges, orphaned accounts left active after employees leave, weak authentication methods without MFA, and shadow IT. Add in poor access reviews and compliance gaps, and you’re looking at real threats like unauthorized access, data breaches, and even regulatory penalties.