Top 9 IAM Best Practices for Secure Access in 2026

Identity and Access Management (IAM) covers the policies that allow people access to digital resources that your organization uses. IAM defines who has access to what applications and systems.
IAM has two main components:
- Identity Management: Verifying who users are with credentials to authenticate those users' identities before they access the systems.
- Access Management: Controlling what authenticated users can use, based on their roles and responsibilities within the organization.
In today's digital world, and for enterprises that face continuous changes in security threats, implementing identity access management best practices has become a necessity. Having an identity access management strategy provides the basis for fortifying your sensitive resources, achieving regulatory compliance, and enabling secure digital transformation. In the latest Verizon DBIR report this year, it showed that identity breaches represented 84% of all security breach incidents.
Key takeaways:
- Understand IAM fundamentals, implementation approaches, and common mistakes
- Discover essential authentication methods that protect against credential compromise
- Learn access control strategies that minimize your organization's attack surface
- Implement automated user lifecycle management across your technology ecosystem
- Adopt Zero Trust principles for a more resilient security architecture
- Integrate governance capabilities to maintain continuous compliance
- Explore emerging technologies, reshaping identity security
- See real-world applications across different industry sectors
What Is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a comprehensive framework of policies, processes, and technologies that enables organizations to manage digital identities and control user access to critical systems and resources. IAM systems verify who users are (authentication), determine what they can access (authorization), manage their identities throughout their lifecycle, and monitor their activities for security and compliance purposes.
A robust IAM framework sits at the intersection of security, operational efficiency, and user experience-protecting sensitive assets while ensuring seamless access for legitimate users. As digital environments grow more complex with cloud migrations, remote work, and third-party integrations, IAM best practices have evolved from simple password policies to sophisticated, context-aware security systems.
For example, in a SaaS application like an HR system (such as Workday) or a finance tool (like QuickBooks), IAM prevents users from accessing the entire application. For example, a recruiter may only be able to access an employee's record. Meanwhile, a finance executive may be allowed to only view the budget items, which allows the company to manage access properly and leave sensitive information restricted. IAM guarantees that the user has the appropriate permissions based on their roles, responsibilities, or job requirements, and makes sure they do not allow free access to sensitive areas they do not have permission to access.
9 Core IAM Best Practices for Identity Security
Organizations seeking to strengthen their identity management best practices must address multiple dimensions of access security. The following nine practices represent the industry consensus on establishing a resilient identity security posture that balances protection with productivity.
1. Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) prompts users to provide two or more verification factors to access resources, applications, or accounts. MFA security requires either something the user knows (an account's password), something the user has (a security token or a mobile device), and/or something the user is (biometric verification).
MFA is one of the best defences against credential-based attacks by adding additional layers of verification beyond the user's password. Even if an attacker gets their hands on your password (by means of phishing, data breaches, etc.), they will still not be able to fully use the account on offer until those additional authentication factors are verified. This dramatically reduces the risk of unauthorized access and improves an organization's overall security posture
Implementing MFA helps organizations:
- Prevent unauthorized access even when passwords are compromised
- Meet regulatory compliance requirements across various industries
- Protect sensitive data from credential-based attacks
- Secure remote access to corporate resources
- Create a foundation for more advanced security models
Enabling MFA in your organization:
- Offers enhanced security with more layers than 2FA
- Ensures the identity of consumers is safeguarded against attacks
- Aligns with regulatory compliance standards
- Boasts straightforward implementation
- Integrates seamlessly with Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions
- Enhances security measures, even in remote work environments
As per research by Microsoft, published in August 2019, MFA stops over 99.9% of account compromise attempts.
Tech Prescient's Identity Confluence platform is building out its own native MFA tool while providing support for risk-based authentication, which adjusts security requirements based on contextual factors like location, device, and behaviour.
2. Apply Least Privilege & Just-in-Time Access
Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege (PoLP) provides users with the least amount of access necessary to perform their work functions – this is better access management best practice. When we discuss least privilege, we suggest limiting user access rights solely to what access is necessary for that specific scope the user is functioning within. That is, least privilege limits user permissions based on their job role, preventing excessive access to sensitive systems and data. Organizations execute this by assessing permissions in scheduled access reviews, creating fine-grained permissions, and revoking or disabling access rights that are no longer needed by users. When users are assigned excessive permissions, if their credentials are compromised, the potential damage can be significant. When companies limit access rights, they can reduce the attack surface and contain the impact that is possible when a user account is compromised.
Just-in-Time Access
Just-in-Time (JIT) access provides temporary, elevated privileges only when a user needs access for a specific job function, rather than giving that user standing or permanent access. JIT creates a temporary, time-bound access notification along with automated approvals and expiration processes. The user who needs privileged access will request the access at the time needed, will receive approval, will then have the elevated rights are active for a predefined time range, and after which the access will automatically expire. This model can reduce the risk of granting a user permanent privileged access, which can be a significant risk if the individual does not require access to the privileges daily, while still allowing productivity, but with less exposed security via unwanted privileged account access.
Implementing these approaches requires:
- Regular entitlement reviews
- Role mining and optimization
- Time-bound privileged access
- Automated access expiration
- Context-aware authorization policies
Organizations that adopt JIT access report a potential 90% decrease in standing privileges and a much smaller attack surface. Research by StrongDM published in 2023, 85% of credentials had not been used in the last 90 days, stressing the importance of removing unnecessary standing privileges. Tech Prescient's Identity Confluence platform offers built-in risk scoring that automatically identifies excessive permissions and recommends right-sizing options while providing temporary elevated access with automated workflows.
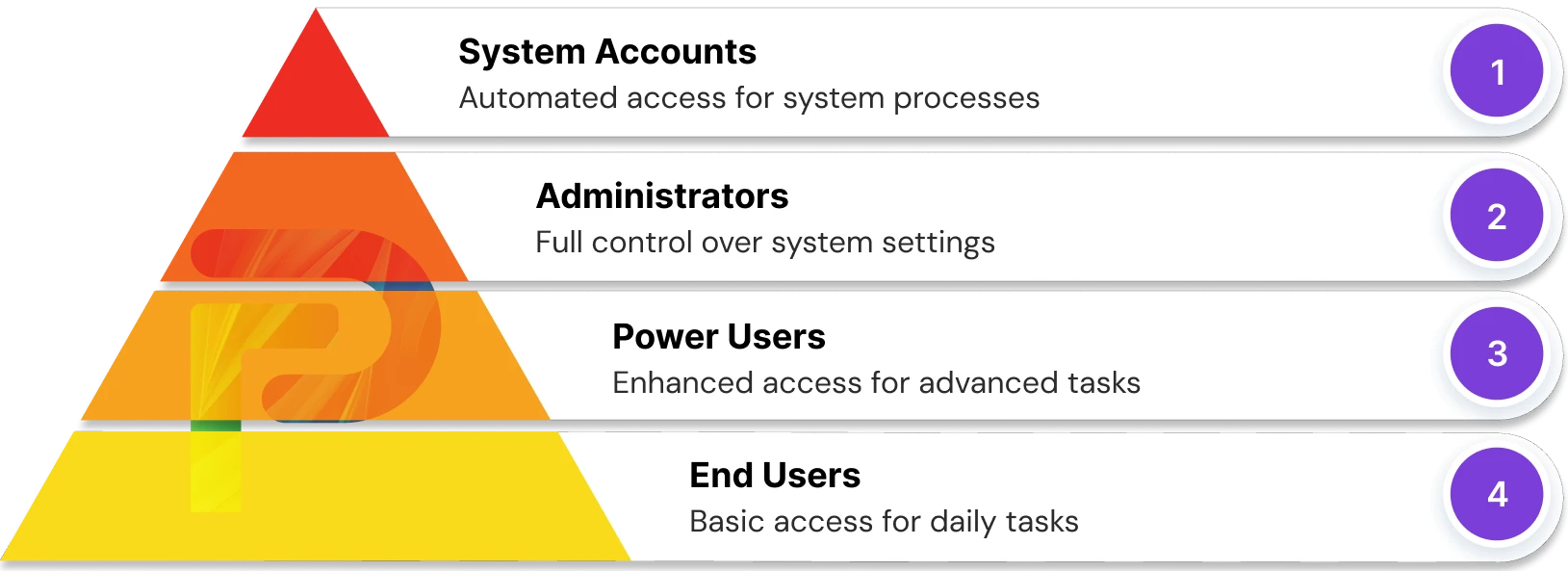
3. Automate User Provisioning and De-Provisioning
Manual identity lifecycle management causes inefficiencies, mistakes, and security gaps that can be eliminated through automated processes, an important IAM best practice—especially critical for scaling organizations.
Provisioning encompasses creating user accounts and granting users the required level of system access permissions. Appropriately provisioning access means creating user identities in directories, assigning application licenses, and role-based permissions to multiple systems for an employee coming on board or moving to a different role within the organization.
De-provisioning means removing all access and accounts once employment is terminated at some level with the organization. This means disabling authentication credentials in some form, removing application licences, and removing system access to prevent unauthorized use after the employee no longer works with the organization.
Automated provisioning enables employees to receive appropriate access as soon as they are hired or change roles. Automated de-provisioning instantly removes all access for employees during the offboarding process.
The benefits extend beyond security to operational efficiency:
- Reduction in onboarding time from days to minutes
- Elimination of orphaned accounts
- Consistent application of access policies
- Decreased helpdesk burden
- Comprehensive audit trails for compliance
Organizations that implement automated provisioning report an average 85% decrease in provisioning time, allowing new employees to be productive from day one. Identity Confluence's User Lifecycle Management module integrates with HR systems like Workday and SAP SuccessFactors to transform HR events into automated access workflows, creating a single source of truth for identity governance across the enterprise.
4. Implement Role-Based & Attribute-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) represent complementary approaches to structuring access permissions. RBAC allows authorization to assign permissions based on job responsibilities and create standard access profiles aligned with business functions. For example, the entire finance department will be assigned the same base permissions for completing financial transactions in financial applications. This particular application has been straightforward and consistent, enabling effective administration with the same access to financial applications by all members of the finance team as they perform their job responsibilities. It is reasonable to assume that the environment is relatively stable and again, the organization has been clear about its structure, rules, and policies in order for the RBAC model to work effectively.
On the other hand, Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) has the potential to offer expanded ability to support dynamic and context-sensitive decisions. ABAC will evaluate many attributes at the point of access rather than simply relying on a role. In fact, ABAC will evaluate several different attributes at the time of access – user attributes (department; security clearance/privileges; certification), resource attributes (level of sensitivity; data classification), environment attributes (day of week; location of user; device type), and organization attributes (segregation of duties policies; regulations for securing privileged information). ABAC can form a flexible security model, which can change with changing context, while offering regimented access controls.
Modern identity management best practices increasingly favour a hybrid approach:
- RBAC for broad access categorization
- ABAC for fine-grained, contextual permissions
- Dynamic assignments based on current conditions
- Continuous authorization validation
This hybrid solution strikes the right balance of security and usability for any organization, big or small.
5. Centralize IAM with Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On (SSO) has evolved from a convenience feature to a security imperative. Centralizing authentication through SSO provides:
- Consistent security policy enforcement
- Reduced password fatigue and unsafe practices
- Comprehensive visibility into access patterns
- Streamlined user experience
- Simplified compliance reporting
Implementing SSO as an identity and access management best practice requires careful planning:
- Federation with cloud applications via SAML, OIDC, or WS-Fed
- Integration with on-premises applications
- Session management and timeout policies
- Risk-based authentication triggers
- Centralized monitoring and analytics
Identity Confluence's integration-ready architecture supports all major federation protocols and offers pre-built connectors for over 50 cloud and on-premise applications, enabling rapid deployment while maintaining security integrity.
6. Adopt Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication represents the convergence of enhanced security and improved user experience-eliminating the primary vulnerability of traditional systems while reducing friction. Modern implementations leverage:
- FIDO2 WebAuthn standards
- Biometric factors (fingerprint, facial recognition)
- Hardware security keys
- Certificate-based authentication
- Mobile device verification
Organizations implementing passwordless solutions report up to a 50% reduction in authentication-related support tickets and significant improvements in both security posture and user satisfaction. This emerging IAM best practice directly addresses the limitations of password-based systems that remain vulnerable to credential stuffing, phishing, and brute force attacks.
Tech Prescient's Identity Confluence platform supports multiple passwordless authentication methods while providing adaptive policies that can require additional verification based on contextual risk factors.
7. Monitor, Audit & Conduct Regular Reviews
Continuous monitoring and periodic reviews transform IAM from a static security control into a dynamic, responsive system, a critical IAM security best practice for maintaining alignment between configured access and actual business requirements.
Effective monitoring and auditing practices include:
- Real-time activity logging and alerting
- Behavioral analytics to detect anomalies
- Scheduled access certification campaigns
- Separation of duties (SoD) validation
- Comprehensive audit trails for regulatory compliance
Identity Confluence's Identity Analytics & Risk Insights module leverages machine learning to score user risk, highlight anomalies, and proactively surface potential security issues before they escalate into breaches. The upcoming Access Reviews & Certifications feature will offer one-click attestation workflows and pre-configured compliance reports tailored to frameworks like SOX, GDPR, and HIPAA.
8. Embrace Zero Trust Security Model
The Zero Trust security model emphasizes a few guiding principles that redefine the identity management best practices: don't trust, always verify, assume breach, and least-privilege access. Instead of relying on implicit trust based on the location of a user on a network or the ownership of an asset, Zero Trust requires strict verification of identity regardless of where access attempts are originating from.
By implementing Zero Trust principles, organizations ensure that users are who they say they are before giving them access to resources, which adds layers of continuous authentication and authorization, ultimately reducing the threats of unauthorized access and extending lateral movement in the event a network's perimeter is bypassed.
Zero Trust principles move IAM from a perimeter-based approach to an all-encompassing, holistic security framework where:
- Identity becomes the new perimeter
- Authentication and authorization occur continuously
- Context informs access decisions
- Lateral movement is constrained
- Micro-segmentation limits breach impact
Implementing Zero Trust requires:
- Strong identity verification for all users
- Device health validation
- Least privilege access enforcement
- Microsegmentation of networks
- Continuous monitoring and validation
Tech Prescient's Identity Confluence platform was architected with Zero Trust principles at its core, providing the continuous verification, least privilege enforcement, and contextual access decisions essential for modern security postures.
9. Educate and Train Employees
While technical controls form the foundation of IAM security, the human element remains critical. Regular security awareness training strengthens the effectiveness of IAM best practices by ensuring users understand:
- The importance of identity security protocols
- How to recognize phishing and social engineering attempts
- Proper handling of credentials and authentication factors
- Procedures for requesting and reviewing access
- Responsibility for reporting suspicious activities
Companies with formal security awareness training programmes experience, on average, 70% fewer successful attacks as compared to companies with no formal education initiatives. Identity Confluence contributes to this compelling statistic by providing intuitive interfaces and clear workflows to build security best practices into daily activities.
10. Integrate Identity Governance and Administration (IGA)
IAM assists organizations with many security activities, but Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) offers additional required certification campaigns, policy enforcement, and separation of duties controls to help organizations manage regulatory obligations and reduce risk.
Tech Prescient's Identity Confluence platform provides IAM and IGA capabilities within a single solution, reducing complexity while ensuring security policy is systematically enforced across environments.
Common IAM Mistakes to Avoid
Even organizations with mature security programmes can undermine their IAM best practices through common implementation errors:
- Over-permissioning users: Granting excessive access rights creates unnecessary risk exposure. Identity Confluence's risk scoring automatically identifies and flags over-privileged accounts.
- Ignoring de-provisioning: Failing to promptly revoke access for departing employees creates orphaned accounts vulnerable to exploitation. Tech Prescient's automated lifecycle management ensures immediate access revocation.
- Treating MFA as optional: Allowing exceptions undermines security posture. According to Okta, organizations that treat MFA as an optional experience have 3-4 times more security incidents than those with universal enforcement. Identity Confluence enables phased MFA rollouts with comprehensive exception tracking.
- Poor integration with HR systems: Relying on manual processes creates delays and errors. Identity Confluence's pre-built connectors establish reliable, automated synchronization with authoritative sources.
- Neglecting regular access reviews: Allowing entitlement drift compromises least privilege principles. Tech Prescient's upcoming certification campaigns automate the review process with intelligent recommendations.
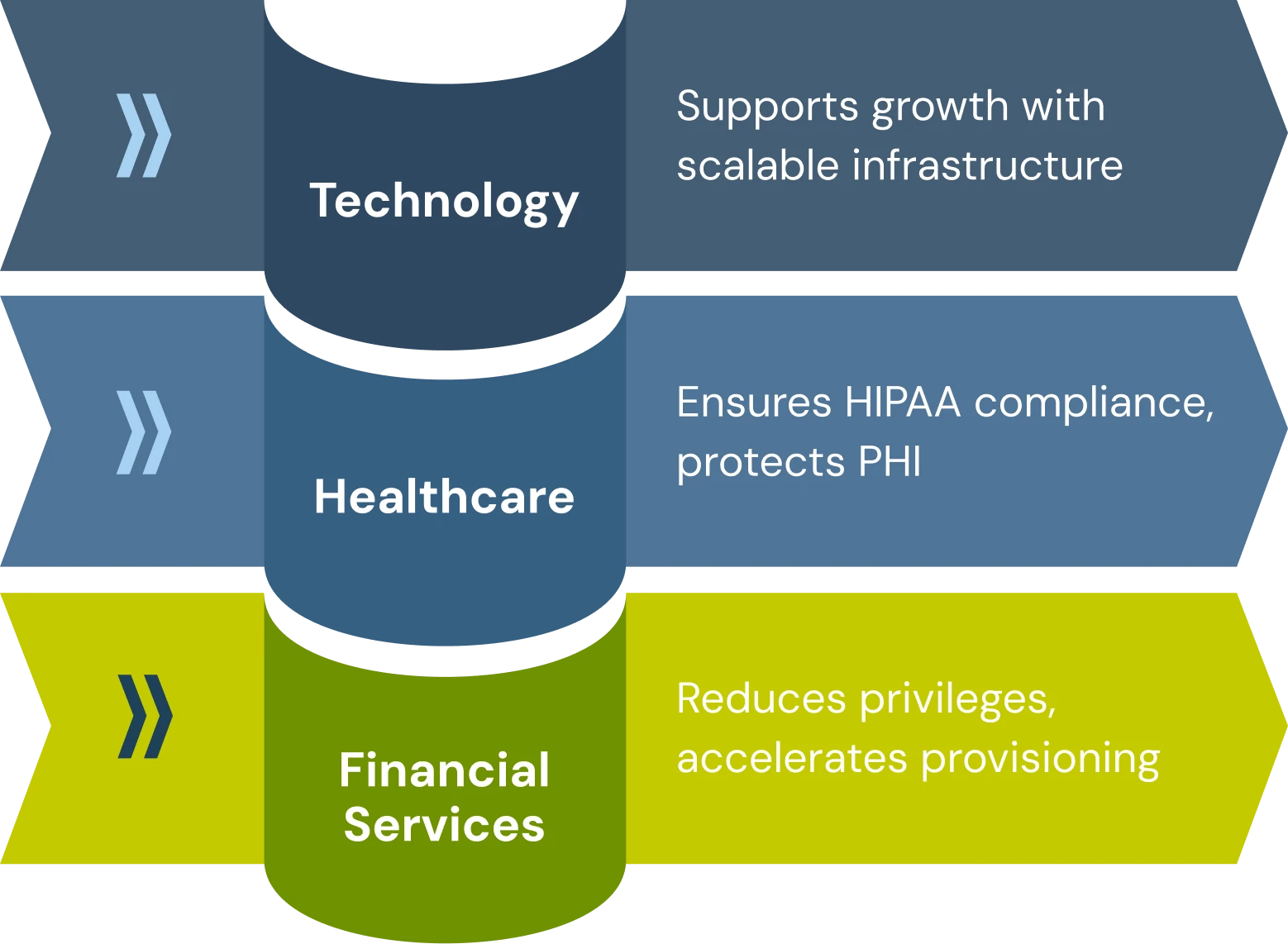
IAM in Action: Industry Use Cases
- Financial Services
A leading financial institution implemented IAM best practices to address regulatory requirements and protect sensitive financial applications. By deploying Identity Confluence's User Lifecycle Management and Just-in-Time access, they achieved:
- 99.9% reduction in standing privileges
- 85% decrease in provisioning time
- Comprehensive audit evidence for regulatory examinations
- Elimination of old orphaned accounts from contractor access
- Healthcare
A multi-facility healthcare system was able to enhance HIPAA compliance and protect patient information by advancing its identity and access management processes. The organization implemented Identity Confluence and offered role-based access control to align functional roles with specific clinical functions so that providers only accessed patient records in relation to their treatment of the patient. Access rights were automatically synchronized with the credentialing of practitioners, and access was revoked immediately when a person left employment, addressing lapses in security that normally took a distressed a few days to close. Detailed audit logs provided the compliance auditors with evidence, and preparation time for regulatory review was reduced significantly. Their implementation of Identity Confluence delivered:
- Role-based access control aligned with clinical functions
- Automated provisioning synchronized with credentialing
- Real-time access revocation for departing practitioners
- Continuous monitoring for unusual PHI access patterns
- Comprehensive audit logs for compliance verification
- SaaS/Technology
A technology company enjoying rapid growth adopted identity management best practices to grow with speed and security. Identity Confluence provided an SSO integration across its cloud applications ecosystem to reduce login friction while also increasing security. The company automated its onboarding workflows with its HRIS, reducing provisioning time from days to minutes and ultimately removing access errors during its rapid hiring process. For the company, this automation also helped manage their 300% year-over-year growth without increasing security costs or compromising their security posture. Identity Confluence provided:
- SSO integration across their cloud application ecosystem
- Automated onboarding aligned with their HRIS system
- Developer-friendly APIs for custom application integration
- Risk-based authentication for sensitive operations
- Scalable identity infrastructure supporting 300% annual growth
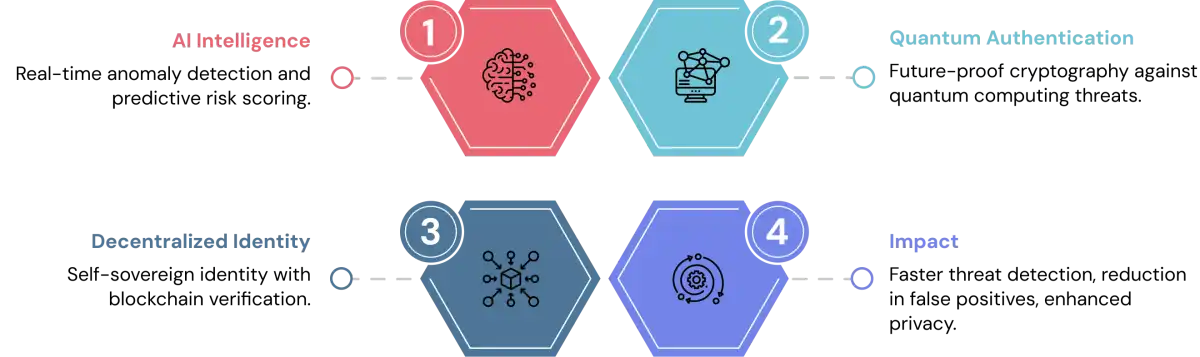
Future of IAM: AI, Automation & Quantum-Resistant Security
The identity security landscape continues to evolve, with several emerging trends reshaping IAM best practices:
AI-Driven Identity Intelligence
Machine learning algorithms are transforming IAM from static rule sets to dynamic, intelligent systems capable of:
- Detecting anomalous access patterns in real-time
- Predicting potential security incidents before they occur
- Optimizing role definitions through behavioral analysis
- Automating routine access decisions
- Providing contextual, risk-based authentication
Quantum-Resistant Authentication
With security technologies continuing to advance, proactive organizations should think about future-proofing their authentication systems. While threats from quantum computing to current cryptography are still a way off, identity solutions must be able to build in new security protocols and keep those flexible as standards evolve.
Decentralized Identity
Self-sovereign identity models based on blockchain and verifiable credentials are emerging as potential solutions for:
- Cross-organizational identity verification
- Privacy-preserving authentication
- User-controlled attribute sharing
- Immutable credential validation
- Reduced dependency on central identity providers
Identity Confluence Identity Confluence assists organizations in anticipation of emerging security issues with actionable solutions:
- Intelligent threat detection that identifies anomalous access behavior that traditional systems would overlook
- Agile security model by being able to pivot when new standards emerge and usually with little to no real implementation changes
- Trusted identity verification seamlessly across all organizational demarcations
- Holistic protection against current and future security threats
Conclusion: Building a Secure IAM Framework
Implementing robust identity access management best practices requires a strategic, layered approach that balances security, usability, and compliance. Organizations must recognize IAM not as a one-time project but as a continuous programme essential to digital security.
The most successful implementations share common characteristics:
- Executive sponsorship and clear governance
- Alignment between business and security objectives
- Phased implementation with measurable outcomes
- Regular reassessment and optimization
- User-centered design that enhances adoption
By adopting these nine core IAM best practices, organizations create a resilient foundation for identity security that adapts to evolving threats while enabling digital transformation. For enterprises seeking to mature their IAM capabilities into comprehensive governance, the natural evolution leads toward Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) frameworks that add policy enforcement, segregation of duties controls, and comprehensive compliance management.
Identity Confluence from Tech Prescient jointly provides IAM and IGA functions in a single unified solution. This unique combination provides the security controls of traditional access management and the governance, compliance, and lifecycle management capabilities of IGA.
Final Thoughts
The Identity Confluence interface integrates multiple solutions and tools while giving security and IT teams the freedom and intelligence to make best practice decisions around protecting assets and allowing business to grow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
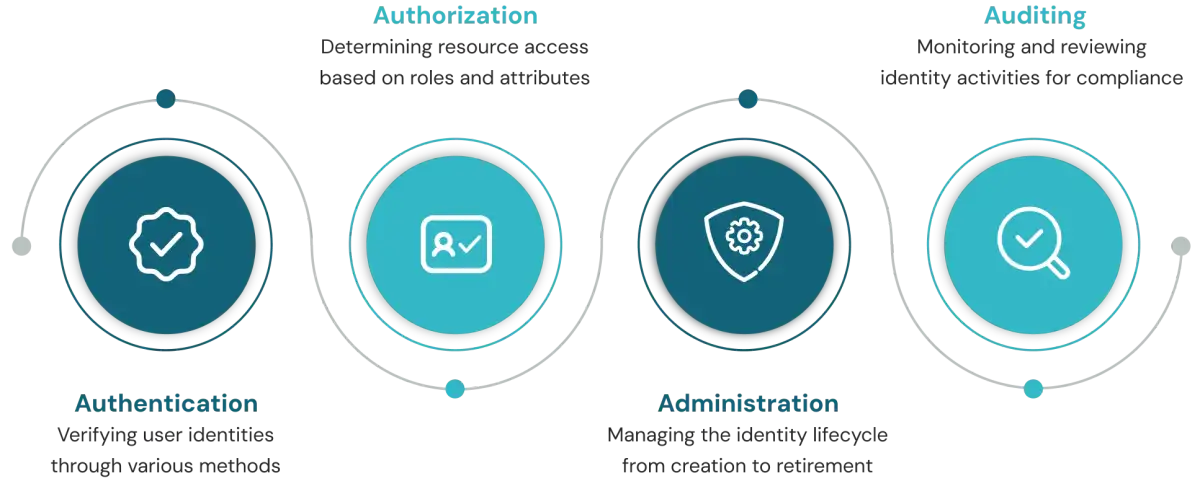
1. What are the 4 pillars of identity and access management?
Authentication, authorization, administration, and auditing form the four fundamental pillars of IAM. Authentication verifies identity claims, authorization determines access rights, administration manages the identity lifecycle, and auditing provides visibility and compliance evidence.2. What is the best practice for identity management?
Enforcing least privilege access, implementing phishing-resistant MFA, automating provisioning and de-provisioning processes, and conducting regular access reviews represent the core best practices for effective identity management in today's threat landscape.3. What are the 4 A's of IAM?
Authentication, authorization, administration, and audit comprise the 4 A's of IAM, representing a critical function within the identity security framework. Modern implementations integrate these functions within a cohesive governance structure.4. What are the three principles of IAM?
The three foundational principles of IAM are to verify identity through strong authentication, enforce least privilege access, and continuously monitor all identity and access activities. These principles form the cornerstone of effective identity security programmes.5. Is IAM the same as IGA?
No-IAM (Identity and Access Management) focuses on managing digital identities and controlling access, while IGA (Identity Governance and Administration) extends these capabilities with governance, compliance, and lifecycle management functions. IGA encompasses IAM while adding policy enforcement, access certification, role management, and comprehensive audit capabilities.6. What is the advantage of a centralized IAM approach?
A centralized IAM approach provides uniform user provisioning, consistent security policies, streamlined administration, comprehensive visibility, and simplified compliance reporting across all systems and applications, reducing security gaps and administrative overhead.7. How often should organizations conduct access reviews?
Organizations should conduct access reviews at least quarterly for sensitive systems and annually for standard access, with additional reviews triggered by significant organizational changes, as recommended by both Okta and StrongDM.8. What role does automation play in modern IAM?
Automation is critical for scalable IAM, eliminating manual errors in provisioning/deprovisioning, ensuring consistent policy application, reducing administrative overhead, providing comprehensive audit trails, and enabling rapid response to security incidents.