Benefits of Identity and Access Management (IAM)

Identity and Access Management (IAM) serves as the foundation of modern cybersecurity, bringing together authentication, authorization, and identity lifecycle management within a unified framework. It ensures that only verified users and trusted services can access your SaaS applications, critical systems, and sensitive data. Through the enforcement of least privilege principles, automation of access reviews, implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA), and maintenance of detailed audit trails, IAM helps reduce breach risks, streamline compliance efforts, and enable organizations to pursue secure digital transformation with confidence.
Unlike traditional access systems, Identity and Access Management (IAM) eliminates the need to grant users blanket access to entire software environments, reducing repetitive permission assignments. It enforces granular access control by functioning as a centralized gatekeeper that authenticates user identities using verified credentials. This authentication mechanism strengthens security by validating each user’s identity and ensuring only authorized individuals gain access to specific resources.
According to Indusface's 2025 cybersecurity research, 80% of data breaches include stolen or abused privileged credentials, underscoring the need for identity management in protecting enterprises. This elevates IAM from a mere security tool to a fundamental layer of digital trust. Throughout this blog, we'll look at how IAM offers these benefits in greater detail.
Key Takeaways:
-
IAM strengthens security by ensuring only the right users get the right access at the right time.
-
It boosts productivity through automation, SSO, and simplified access management.
-
IAM streamlines compliance with built-in audit trails and policy enforcement.
-
It enhances user experience with secure, seamless access across devices and teams.
-
The future of IAM lies in Zero Trust, cloud adoption, and AI-driven automation.
What Is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a security framework that defines and manages digital identities across an organization. It ensures that users can access systems and data securely and appropriately, while unauthorized individuals are kept out. By combining user verification, access control, and lifecycle management, IAM helps protect sensitive assets, streamline user access, and maintain operational efficiency.
IAM and Zero Trust Security
IAM is a key pillar of the Zero Trust security model, which operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Instead of granting blanket access once a user logs in, IAM continuously validates identity and contextual factors like device, location, and activity patterns before allowing entry. This approach minimizes the risk of credential misuse, lateral movement, and insider threats, strengthening the organization’s overall security posture.
Core Functions of IAM
-
Authentication: This process verifies a user’s identity before granting access to systems or data. It typically involves passwords, biometrics, security tokens, or multi-factor authentication (MFA). Strong authentication ensures that only legitimate users can enter the network and helps prevent unauthorized access or credential-based attacks.
-
Authorization: Once a user’s identity is verified, authorization determines what actions and resources they are allowed to access. It defines permissions based on predefined roles, policies, or attributes, ensuring users can interact only with the systems and data relevant to their responsibilities. This helps reduce the likelihood of internal misuse or accidental exposure of sensitive information.
-
Provisioning and Deprovisioning: IAM automates the process of creating, updating, and removing user accounts as employees join, transfer within, or leave the organization. Automated provisioning ensures users receive the right level of access quickly, while deprovisioning immediately revokes access when it’s no longer needed. This prevents orphaned accounts, minimizes security risks, and maintains a clean access environment.
Popular IAM Tools
Organizations often rely on IAM platforms like Okta, Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), and CyberArk to streamline identity management. These tools centralize access control, enforce multi-factor authentication, integrate with cloud and on-premises systems, and provide real-time visibility into user activities, helping IT teams manage digital identities efficiently and securely.
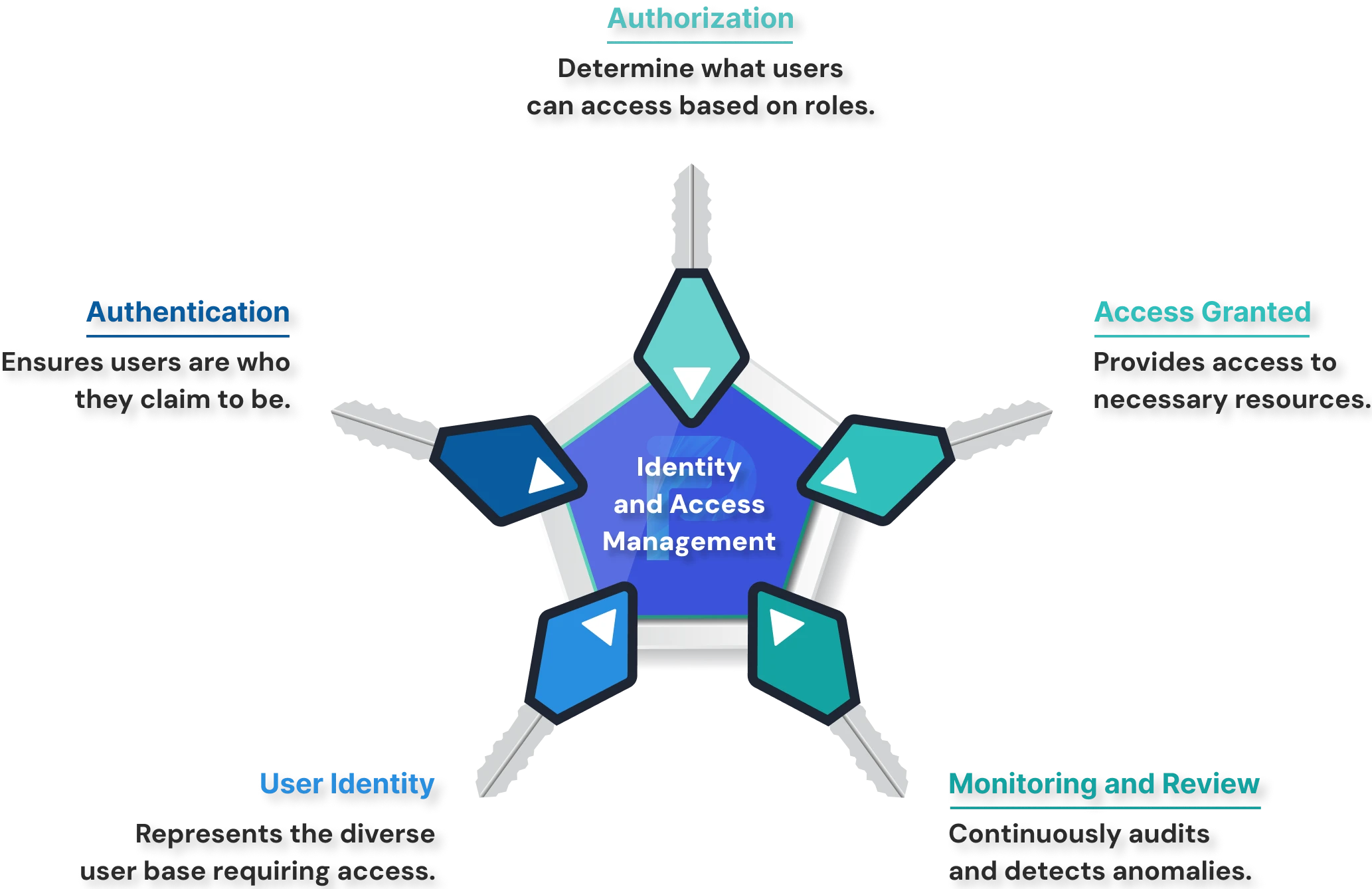
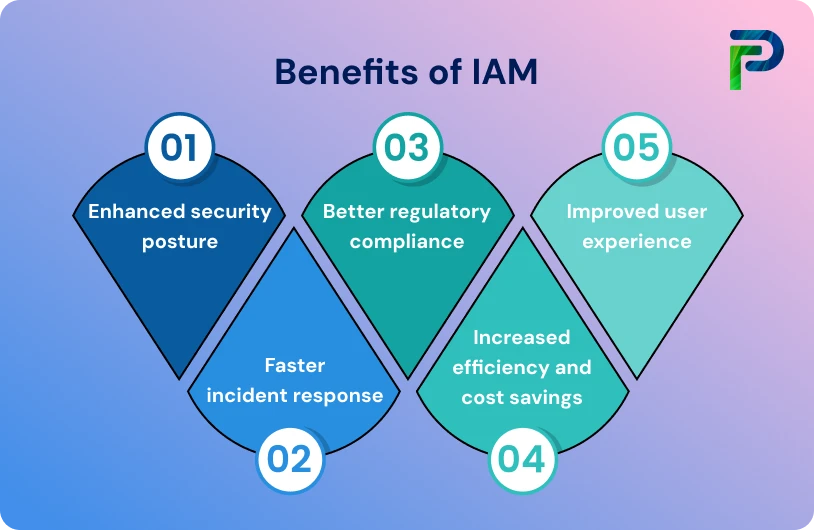
Key Benefits of Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implementing IAM offers more than just secure access control; it transforms how organizations manage users, data, and systems across their digital environment. From strengthening cybersecurity defenses to streamlining IT operations, IAM delivers measurable business and compliance value. Below are the six core benefits that highlight why IAM is a cornerstone of modern enterprise security.
1. Enhanced Security and Risk Mitigation
Effective Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions form the backbone of an organization’s cybersecurity posture by preventing unauthorized access and continuously validating user identities. By enforcing mechanisms such as Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), IAM minimizes risks from credential misuse and insider threats while aligning with Zero Trust principles.
-
Single Sign-On (SSO):
Single Sign-On simplifies user authentication across multiple applications and systems with a single set of credentials. It relies on a trusted identity provider to verify users, reducing password fatigue, minimizing credential reuse, and enhancing identity protection across the enterprise. With centralized authentication, organizations can more easily monitor login activity and detect unusual access behavior. -
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Mult-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a critical layer of verification by requiring users to provide multiple credentials before accessing systems, such as something they know (password), something they have (a one-time code or token), and something they are (biometric data). This layered approach drastically reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access from compromised passwords or phishing attempts. -
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) enforces the principle of least privilege (PoLP) by granting users access strictly based on their roles, responsibilities, and authority levels. System administrators can define and manage permissions according to job functions, ensuring users only access the information and tools required for their work. This containment approach limits lateral movement during a breach and strengthens overall compliance. -
Connection to Zero Trust Architecture:
In a Zero Trust environment, no user or device is automatically trusted. Verification is continuous, regardless of network location. IAM plays a pivotal role in enforcing this model by constantly assessing and authenticating users’ access requests, validating context such as device, location, and behavior, and restricting access dynamically. By combining SSO, MFA, and RBAC under Zero Trust principles, organizations achieve robust identity assurance, reduce attack surfaces, and improve visibility into user activity for proactive threat detection.
2. Streamlined Access Management and Productivity
Centralized Identity and Access Management (IAM) significantly improves operational efficiency while enhancing the user experience. By automating access workflows, IAM ensures that employees, contractors, and partners can access the systems and applications they need promptly, reducing bottlenecks and manual IT intervention.
-
Automated Provisioning and Deprovisioning:
IAM platforms streamline the onboarding and offboarding processes by automatically granting or revoking access based on a user’s role or employment status. This reduces administrative overhead, minimizes the risk of orphaned accounts, and ensures that users have the correct permissions from day one. -
Single Sign-On (SSO) for Better User Experience:
SSO allows users to log in once and gain access to multiple applications without repeated password entries. This not only saves time but also decreases password fatigue, helping prevent weak password practices that could compromise security. -
Fewer Support Tickets and IT Workload Reduction:
Automated access management directly translates into fewer password reset requests and other routine IT tickets. IT teams can focus on higher-value tasks instead of manually managing credentials, improving overall productivity and operational efficiency. -
Integration with HR and Enterprise Systems:
By syncing IAM with HR systems or other internal directories, access rights automatically adjust as employees change roles or departments. This ensures that users always have appropriate access aligned with their responsibilities while maintaining security and compliance standards.
Organizations implementing centralized IAM report faster onboarding, smoother role transitions, and a measurable reduction in administrative tasks. Employees enjoy seamless access, and IT teams benefit from lower operational strain, allowing the business to scale efficiently without compromising security.
3. Simplified Compliance and Audit Readiness
Identity and Access Management (IAM) plays a vital role in helping organizations meet regulatory and compliance requirements consistently and efficiently. By centralizing and automating access control, IAM ensures that policies are enforced uniformly across all users, systems, and applications, reducing the risk of non-compliance and audit failures.
-
Automated Access Logs and Audit Trails:
IAM solutions maintain detailed logs of who accessed which systems, when, and what actions they performed. These comprehensive audit trails simplify reporting, make it easier to detect unusual or unauthorized activity, and provide a clear record for internal reviews and external audits. -
Regulatory Alignment:
IAM frameworks are critical for aligning with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. By enforcing role-based access and ensuring only authorized personnel can view sensitive data, IAM supports data protection, privacy mandates, and compliance verification. -
Streamlined Audit Processes:
Centralized IAM tools reduce the manual effort involved in audit preparation. System administrators can quickly generate reports that demonstrate compliance, track policy enforcement, and provide evidence of proper access management. This not only saves time but also strengthens the organization’s credibility during audits and certifications.
Organizations leveraging IAM for compliance see faster audit cycles, improved regulatory alignment, and reduced risk of penalties. By automating access reviews and maintaining transparent records, IAM enables teams to focus on strategic initiatives while ensuring compliance remains accurate and consistent across the enterprise.
4. Improved User Experience and Collaboration
Identity and Access Management (IAM) not only strengthens security but also enhances productivity and collaboration within organizations. By centralizing access control and implementing modern authentication methods, IAM ensures that employees, partners, and external collaborators can securely access the resources they need without unnecessary friction.
-
Single Sign-On (SSO) and Federated Identity:
SSO allows users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications, reducing login complexity and minimizing password fatigue. Federated identity extends this convenience to external partners, enabling seamless collaboration across organizations while maintaining strict access control. -
Secure External Partner Access:
IAM frameworks allow businesses to provide controlled access to contractors, vendors, or partners without compromising sensitive data. Role-based permissions and temporary access features ensure external collaborators can complete tasks efficiently while adhering to security policies. -
Remote Work Enablement:
With more organizations supporting hybrid or fully remote work environments, IAM plays a critical role in providing secure access from anywhere. Conditional access policies and context-aware authentication maintain security while enabling employees to work without interruptions. -
Measurable Productivity Gains:
By simplifying access and reducing login challenges, IAM helps decrease helpdesk tickets and boosts employee satisfaction. Many organizations report significant improvements, such as up to 25% fewer login issues, allowing teams to focus on strategic tasks rather than resolving access problems.
Overall, IAM fosters a secure, collaborative, and user-friendly environment. Employees and partners can work efficiently, IT teams spend less time on routine access management, and organizations can maintain high productivity without sacrificing security.
5. Cost Savings and Operational Efficiency
Identity and Access Management (IAM) not only strengthens security but also drives significant operational efficiency and cost reduction. By automating routine access processes, IAM helps organizations minimize manual work, reduce errors, and prevent costly security incidents.
-
Reduction in Password Reset Tickets:
A major source of IT workload comes from users forgetting passwords or experiencing login issues. IAM solutions, especially those with Single Sign-On (SSO) and self-service password reset capabilities, drastically reduce these requests, freeing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives. -
Decreased Manual IT Tasks:
Automated provisioning and deprovisioning of user accounts streamline onboarding and offboarding processes. By syncing with HR systems or enterprise directories, IAM ensures employees receive the right access from day one, eliminating manual interventions and potential human errors. -
Preventing Costly Security Breaches:
Controlled access, strong authentication methods, and adherence to the principle of least privilege (PoLP) reduce the risk of data breaches. Avoiding even a single security incident can save an organization millions in fines, remediation, and reputational damage. -
Indirect ROI and Productivity Gains:
Beyond direct cost savings, IAM improves overall productivity. Employees spend less time troubleshooting access issues, IT teams handle fewer routine tickets, and business operations continue smoothly with minimal downtime. These cumulative gains result in measurable operational efficiency and positive return on investment.
Organizations leveraging IAM consistently report lower IT costs, faster onboarding cycles, and reduced exposure to security risks. By combining security with automation, IAM becomes a key driver of both cost efficiency and operational resilience.
6. IAM as the Foundation for Zero Trust Security
Identity and Access Management (IAM) forms the cornerstone of a Zero Trust security framework by ensuring that access to resources is continuously verified and strictly aligned with user roles and context. Instead of assuming trust based on network location or device, Zero Trust relies on IAM to authenticate, authorize, and monitor every user and device attempting to access critical systems.
-
Continuous Authentication and Micro-Segmentation:
IAM enables organizations to implement ongoing verification for users and devices. By combining multi-factor authentication, behavioral analytics, and contextual signals, access decisions are dynamically adjusted. Micro-segmentation further restricts lateral movement, limiting the exposure of sensitive data in case of a breach. -
Context-Based Access Decisions:
Zero Trust leverages IAM to enforce access policies based on multiple contextual factors, including user identity, device type, location, and network state. Access is granted only when all criteria are met, ensuring that employees, contractors, or partners have the minimum privileges required for their tasks. -
Integration with PAM and IGA:
IAM solutions integrate seamlessly with Privileged Access Management (PAM) and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) systems, enabling secure management of high-risk accounts and automated policy enforcement. This integration strengthens control over privileged users and ensures compliance with internal policies and regulatory standards.
By anchoring Zero Trust with robust IAM, organizations achieve stronger security posture, reduce the risk of insider threats, and maintain precise control over sensitive data. Continuous verification and least-privilege enforcement allow businesses to operate securely in increasingly complex, hybrid IT environments.
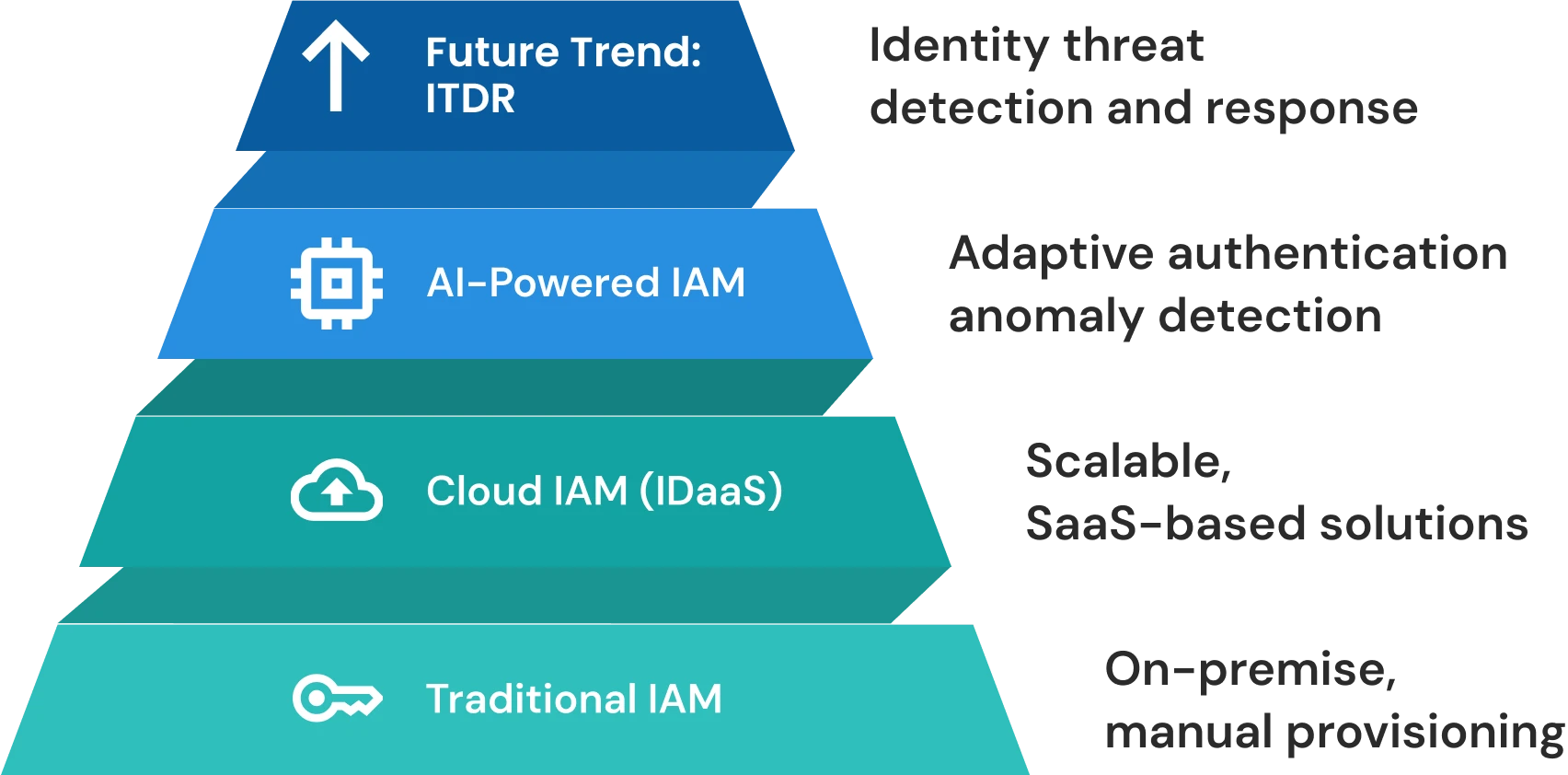
Future of IAM: Cloud, AI, and Automation
The future of Identity and Access Management (IAM) is being shaped by cloud adoption, AI-driven analytics, and intelligent automation. These advancements are enabling organizations to move beyond traditional identity management, creating agile, proactive, and highly secure environments.
-
Shift to Identity-as-a-Service (IDaaS):
Cloud-based IAM, or IDaaS, allows organizations to manage identities and access without the complexity of on-premises infrastructure. By centralizing identity management in the cloud, businesses can scale rapidly, simplify administration, and ensure consistent security across hybrid environments. -
AI-Powered Threat Detection:
Artificial intelligence enhances IAM by analyzing user behavior, detecting anomalies, and identifying potential threats in real-time. AI-based anomaly detection helps prevent unauthorized access, insider threats, and credential misuse before they escalate into breaches. -
Adaptive Authentication:
Next-generation IAM leverages context-aware and adaptive authentication to provide flexible yet secure access. Decisions are based on factors such as device type, location, network, and user behavior, allowing legitimate users to work efficiently while maintaining strong security controls. -
Emerging Trend: Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR):
Organizations are increasingly adopting ITDR frameworks to proactively monitor and respond to identity-based risks. By combining IAM, AI analytics, and automated responses, ITDR provides continuous protection for critical resources against evolving identity threats.
Future-ready IAM ensures seamless user experiences, reduces administrative overhead, and strengthens security posture. Cloud, AI, and automation together make identity management smarter, faster, and more resilient against modern cyber threats.
Final Thoughts
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is no longer just an IT function; it is the backbone of modern cybersecurity. As organizations embrace cloud environments, remote work, and hybrid ecosystems, IAM ensures that every identity is verified, every access request is justified, and every action is monitored. This foundation of trust minimizes risks, simplifies compliance, and enhances productivity across the enterprise.
At the same time, IAM continues to evolve with AI, automation, and Zero Trust principles, giving security teams greater visibility and control than ever before. The future of IAM lies in intelligent, adaptive systems that not only protect against breaches but also enable seamless, secure collaboration.
To see how Tech Prescient, helps enterprises implement next-generation IAM frameworks that balance security, compliance, and user experience –
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the main benefits of Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
IAM enhances security by ensuring that only verified users can access critical systems and data. It simplifies compliance through consistent access policies and audit-ready reporting. With centralized access control, organizations can also streamline operations, reduce administrative overhead, and improve overall efficiency.2. Why is IAM important for organizations?
IAM is essential because it prevents unauthorized access and protects sensitive information across complex digital environments. It supports Zero Trust principles by continuously verifying identities and access privileges, ensuring that every user, device, and connection is authenticated before gaining entry to resources.3. What are the key advantages of IAM tools?
Modern IAM tools bring automation, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and detailed audit trails together to strengthen cybersecurity. They help reduce human error, minimize security risks, and free up IT teams from repetitive tasks. As a result, organizations gain better visibility, control, and efficiency in managing digital identities.4. How does IAM improve compliance?
IAM improves compliance by enforcing consistent access policies, recording user activity, and providing comprehensive audit logs. These capabilities help organizations demonstrate adherence to frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX while reducing the risk of policy violations or data breaches.5. How does IAM support digital transformation?
IAM plays a key role in digital transformation by enabling secure access to cloud applications, remote systems, and hybrid environments. Through identity-based access controls, it ensures that users can collaborate and innovate safely, no matter where they work, while maintaining compliance and data integrity.