What is ASPM (Application Security Posture Management)?

Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) is a modern technique to detect, correlate, and prioritise vulnerabilities across the software development lifecycle. With applications getting more sophisticated, attack surfaces extending, and compliance demands increasing, security teams are frequently overburdened. By integrating data from several technologies into a single view, ASPM gets around this and lets teams concentrate on what matters most.
ASPM acts as a centralized source of truth for application security by consolidating results from various security tools into a single, unified dashboard. This allows teams to prioritize risks based on actual impact, addressing the most critical vulnerabilities first. Meanwhile, automated remediation workflows reduce manual effort and eliminate time wasted on false positives and duplicate issues scattered across different tools.
According to a recent study from Gartner's Innovation Insight, companies in regulated sectors who use AppSec testing now have roughly 29% of them employing ASPM, and that percentage is predicted to rise significantly. Accordingly, complexity, compliance, and scalability are driving ASPM into the mainstream at this critical juncture.
Let's examine ASPM's definition, significance in 2025, potential features, comparison to comparable tools, practical applications, and future developments.
Key Takeaways:
-
ASPM unifies application security tools, risks, and insights into a single view.
-
Rising cloud complexity and compliance needs make ASPM critical in 2025.
-
Core capabilities include visibility, risk prioritization, policy enforcement, and collaboration.
-
ASPM complements other security tools like CSPM, DSPM, and ASOC.
-
It delivers measurable business impact, real-world use cases, and future-ready security with AI and cloud.
ASPM Meaning Explained
Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) is a cybersecurity approach that helps organizations continuously identify, monitor, and improve the security posture of their applications throughout the entire software delivery lifecycle. It unifies insights from multiple AppSec tools into a single, correlated view, enabling risk-based prioritization and streamlined remediation.
While ASPM can mean different things in other domains like Active State Power Management in computing or Airport Surface Performance Metric in aviation, here it specifically refers to cybersecurity ASPM, which focuses on securing applications, code, and infrastructure across hybrid and cloud environments.
In essence, Application Security Posture Management acts as a governance and command platform that integrates with scanning, testing, and monitoring tools to deliver a holistic view of application risk. It consolidates findings from tools like Static Application Security Testing (SAST), Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST), Software Composition Analysis (SCA), and Infrastructure as Code scanners (laC), and helps security teams prioritize vulnerabilities based on exploitability and business impact.
Key functions of ASPM include:
- Continuously assessing and monitoring application security across development and cloud environments.
- Integrating with AppSec tools, CI/CD pipelines, and ticketing systems to provide unified visibility.
- Automating detection, correlation, and prioritization of vulnerabilities based on contextual risk.
- Centralizing policy enforcement to maintain consistent security standards.
- Providing risk-based scoring and contextual insights for faster, more accurate decision-making.
- Tracking architecture and dependency drift to prevent unnoticed vulnerabilities.
- Enabling collaboration between development and security teams with automated remediation workflows.
Advanced ASPM solutions also leverage AI and machine learning to detect emerging threats, predict potential exploits, and recommend proactive measures. By combining automation, integration, and intelligence, ASPM unifies AppSec and infrastructure vulnerability management to ensure security remains continuous, contextual, and scalable across the entire organization.
Why is ASPM Important in 2025?
ASPM arose as a response to the growing complexity of modern application ecosystems, tightening regulatory requirements, and the disconnect between fragmented testing and development tools that introduce inefficiencies and risk.
Traditional application security testing was designed for a different era, when applications were monolithic, built largely on proprietary code, and released on a monthly schedule. Today’s software landscape is vastly different. Modern applications integrate open-source components, APIs, microservices, containers, and infrastructure as code, requiring a diverse set of testing methodologies. However, these tools often operate in silos, making it difficult to coordinate scans, consolidate findings, and manage remediation efficiently.
The challenge intensifies as release cycles accelerate from monthly to weekly or even multiple times per day. Adding the pressure of generating unified reports, passing audits, and maintaining regulatory compliance makes it clear why ASPM has become essential for modern development environments.
According to Gartner, by 2026, nearly 40% of organizations developing proprietary applications will adopt ASPM solutions to streamline AppSec operations and strengthen security posture. This growth is driven by increasing compliance requirements, expanding supply chain risks, and the need for better visibility across hybrid environments.
ASPM provides a structured and scalable way to handle these growing complexities, ensuring that security remains embedded throughout both development and operations. By streamlining and integrating security practices, ASPM addresses the challenges of secure software delivery while driving value across five key areas:
-
Visibility: Create a holistic perspective of your product risk. Identify all repositories and assets to achieve end-to-end visibility throughout your ecosystem with extensive integrations across code repositories, infrastructure, cloud, and container scanners.
-
Risk-Based Prioritization: Correlate findings across tools, enrich them with business context and threat intelligence, and focus on vulnerabilities that pose real-world risk.
-
Remediation Efficiency: Automate ticketing, triage, and escalation to help developers resolve issues faster while reducing manual effort.
-
Automation: Orchestrate DevSecOps workflows at scale with automated scans, guardrails, and policy enforcement throughout CI/CD pipelines.
-
Data-Driven Security: Use analytics and metrics like MTTR and SLA tracking to measure progress, optimize team performance, and continuously mature the organization’s security posture.
Ultimately, ASPM enables enterprises to manage risk proactively, accelerate compliance and reporting, and empower developers to ship secure code without friction.
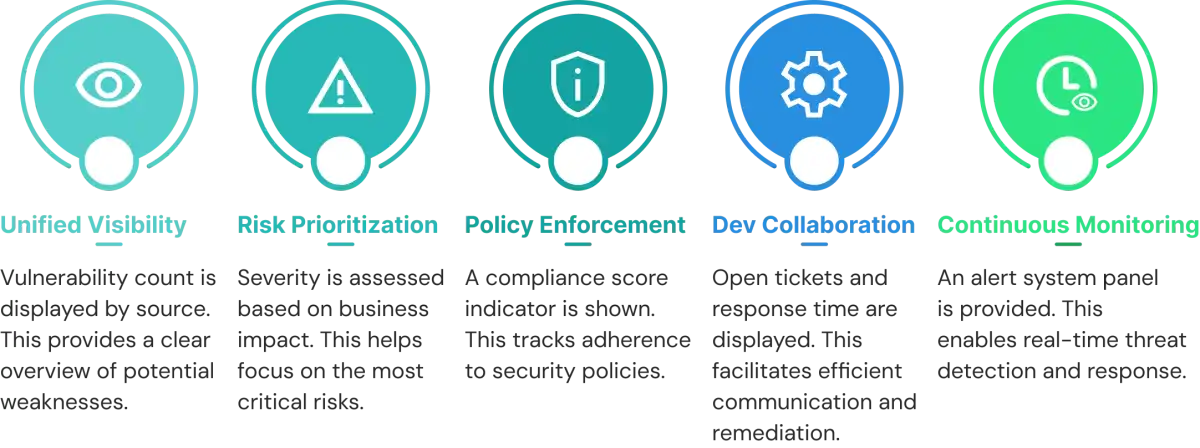
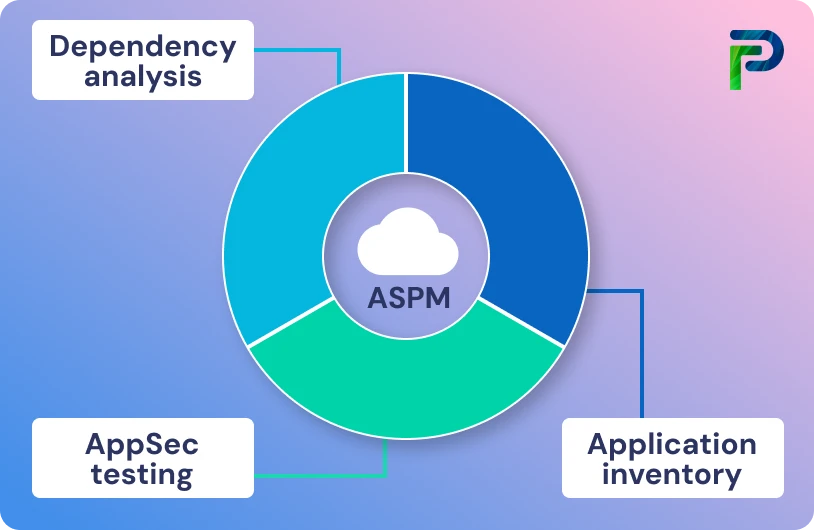
Core ASPM Capabilities
Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) consolidates multiple application security functions into a single, unified system that bridges the gap between tools, teams, and processes. It delivers complete visibility, prioritization, automation, and collaboration across the software development lifecycle, helping organizations maintain a strong and proactive security posture.
1. Unified Visibility
ASPM provides a centralized view of vulnerabilities and security posture across all AppSec tools, including SAST, DAST, SCA, and IaC scanners. By aggregating findings from multiple sources, ASPM eliminates silos and creates a single pane of glass for developers and security teams.
It automatically builds and maintains an up-to-date inventory of all applications, their dependencies, APIs, and services, giving teams a 360-degree view of their ecosystem. This helps uncover misconfigurations, vulnerable components, and exposure points across code, containers, and cloud environments. With contextual insights and metadata, ASPM connects technical risks to business impact, helping teams understand what matters most and why.
2. Risk-Based Prioritization
An effective ASPM solution should deliver a comprehensive view of the organization’s overall risk posture across its entire software landscape. It must offer detailed insights into the location of vulnerable components and applications, the progress of issue remediation, and any existing policy or compliance breaches. In essence, security leaders should be able to use ASPM to audit applications, assess software-related organizational risk, and track key KPIs that reflect the performance and maturity of their AppSec program.
3. Policy Enforcement
ASPM enforces security and compliance policies consistently across the software delivery lifecycle. It aligns organizational guardrails with frameworks like OWASP, PCI DSS, and HIPAA, ensuring every release meets compliance and audit requirements.
Through policy automation, ASPM helps developers build secure applications by design. Security teams define policies once, and ASPM ensures adherence across development, testing, and production environments. It also simplifies compliance reporting by maintaining auditable trails and real-time dashboards tailored to executive, security, and developer needs.
4. Developer Collaboration
ASPM enhances DevSecOps collaboration by integrating directly into existing developer workflows and tools such as CI/CD pipelines, ticketing systems, and communication platforms. Developers receive actionable insights and prioritized issues directly within their tools, minimizing context switching.
It automates remediation workflows such as ticket creation, escalation, and notifications through integrations with systems like Jira or Slack. By embedding security feedback loops early in development, ASPM promotes shift-left security, allowing vulnerabilities to be identified and fixed when they are most cost-effective to address. Moreover, ASPM supports developer enablement through targeted training and in-tool guidance, ensuring teams not only fix issues but also understand the underlying security principles behind them.
5. Continuous Monitoring & Alerts
ASPM continuously monitors applications and their environments to detect emerging vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in real time. It integrates with DevSecOps pipelines to ensure ongoing validation of application integrity as new code, dependencies, or infrastructure changes are introduced.
Advanced platforms provide automated alerting and reporting capabilities, surfacing high-priority issues based on defined risk thresholds. They enable organizations to measure metrics like Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR) and track performance against SLAs, giving leaders data-driven visibility into AppSec progress and maturity.
By combining automation, visibility, and intelligence, ASPM ensures that application security is continuous, proactive, and aligned with the speed of modern software delivery.
ASPM vs Other Security Tools
ASPM does not replace other security platforms. It complements them. Each tool, from Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) to Data Security Posture Management (DSPM), Application Security Orchestration and Correlation (ASOC), and Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP), addresses a distinct layer of the modern security stack. ASPM acts as the unifying layer that bridges these tools by focusing on the application layer. It integrates insights across scanners and systems to provide end-to-end visibility and risk-based prioritization throughout the software development lifecycle.
1. ASPM vs CSPM
The primary distinction between Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) lies in their areas of focus. CSPM is designed to monitor and manage the security posture of cloud-based environments such as IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS. These solutions specialize in identifying cloud configuration and compliance issues, offering visibility into the overall security of cloud ecosystems and the services used to develop or host applications. However, CSPM does not provide detailed insight into the specific security vulnerabilities within the application development process. For instance, it cannot determine whether a cloud-deployed application contains vulnerable components. This is where ASPM becomes essential.
ASPM solutions bridge this gap by giving security and development teams complete visibility into security issues across every phase of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). By aggregating results from various testing stages, from build to production, ASPM tools create a detailed view of an organization’s software inventory and project architecture. This depth of visibility offers precise context and actionable guidance to identify and mitigate risks directly at the source code level.
2. ASPM vs ASOC
Both ASPM (Application Security Posture Management) and ASOC (Application Security Orchestration and Correlation) are designed to streamline application security, but their scope and focus differ.
ASOC focuses on optimizing the testing workflow. It aggregates results from various security tools such as SAST, DAST, and SCA into a unified dashboard, allowing security teams to orchestrate scans, correlate vulnerabilities, and prioritize remediation. In essence, ASOC acts as the coordination hub that synchronizes multiple AppSec tools and provides a consolidated view of detected issues.
ASPM, on the other hand, expands the horizon. It includes everything ASOC offers while adding a comprehensive, DevSecOps-oriented perspective. ASPM continuously evaluates the security posture of applications across the entire software lifecycle by tracking risks, ownership, and remediation progress. Rather than just reporting scan results, ASPM provides contextual insight into business risk and promotes a risk-based and visibility-driven approach to application security.
To put it simply:
-
ASOC = Centralize and streamline your security testing process.
-
ASPM = Extend beyond orchestration to manage and measure your overall application security posture.
ASPM represents the next generation of ASOC, moving from tool coordination to embedding security awareness and risk management into every stage of software development and deployment.
3. ASPM vs CNAPP
CNAPP (Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform) focuses on runtime security by safeguarding applications while they are active and running in the cloud. It brings together capabilities from CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management), CWPP (Cloud Workload Protection Platform), and CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management) to deliver continuous monitoring and real-time protection across your cloud environment. CNAPP identifies container vulnerabilities, enforces Kubernetes and network policies, secures serverless workloads, and ensures cloud configurations remain compliant and resilient. In essence, CNAPP focuses on securing what is already deployed in production.
ASPM (Application Security Posture Management) takes a proactive approach by addressing risks before deployment. It continuously assesses security across the application layer, covering code, containers, and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) files. ASPM helps teams detect and remediate vulnerabilities early in the software development lifecycle (SDLC), reducing the likelihood of issues reaching production. It provides deep visibility into how code, configurations, and third-party dependencies influence the overall security posture, enabling a shift-left strategy that strengthens applications from the ground up.
4. ASPM vs DSPM
ASPM secures the software development lifecycle by identifying vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance gaps across applications and pipelines. Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) focuses on the data layer. It continuously discovers, classifies, and secures sensitive data such as PII, PHI, credentials, or intellectual property across cloud and on-premises environments.
Modern DSPM tools include both passive capabilities, such as continuous data discovery and exposure monitoring, and active capabilities, such as automated remediation and real-time policy enforcement. These tools maintain visibility and control even in complex environments, complementing ASPM’s role in securing the applications that handle that data.
Together, ASPM safeguards your software, while DSPM secures the data behind it.
5. Comparison Summary
| Sr No. | Tool | Primary Focus | Core Function | Stage of Protection | Example Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ASPM | ASPM focuses on the application layer and tracks risks across code and pipelines. | It aggregates scan results, prioritizes issues, and manages security posture. | ASPM protects applications across the SDLC. | It integrates SAST, DAST, and SCA tools, enforces policies, and drives risk-based remediation. |
| 2 | CSPM | CSPM focuses on cloud infrastructure and configurations. | It detects misconfigurations and compliance issues in cloud setups. | CSPM protects during cloud configuration and runtime. | It monitors compliance, scans resources, and alerts on insecure settings. |
| 3 | ASOC | ASOC focuses on orchestrating application security testing. | It coordinates scans, correlates results, and streamlines fixes. | ASOC protects during development and testing. | It consolidates tool outputs, automates scans, and generates remediation reports. |
| 4 | CNAPP | CNAPP focuses on securing cloud-native workloads in production. | It provides real-time monitoring and protection across the cloud. | CNAPP protects applications at runtime. | It detects container issues, enforces Kubernetes policies, secures serverless, and ensures compliance. |
| 5 | DSPM | DSPM focuses on discovering and protecting sensitive data. | It monitors exposure and enforces controls on critical data. | DSPM provides continuous protection across all environments. | It automates data discovery, classifies sensitive data, and remediates exposure risks. |
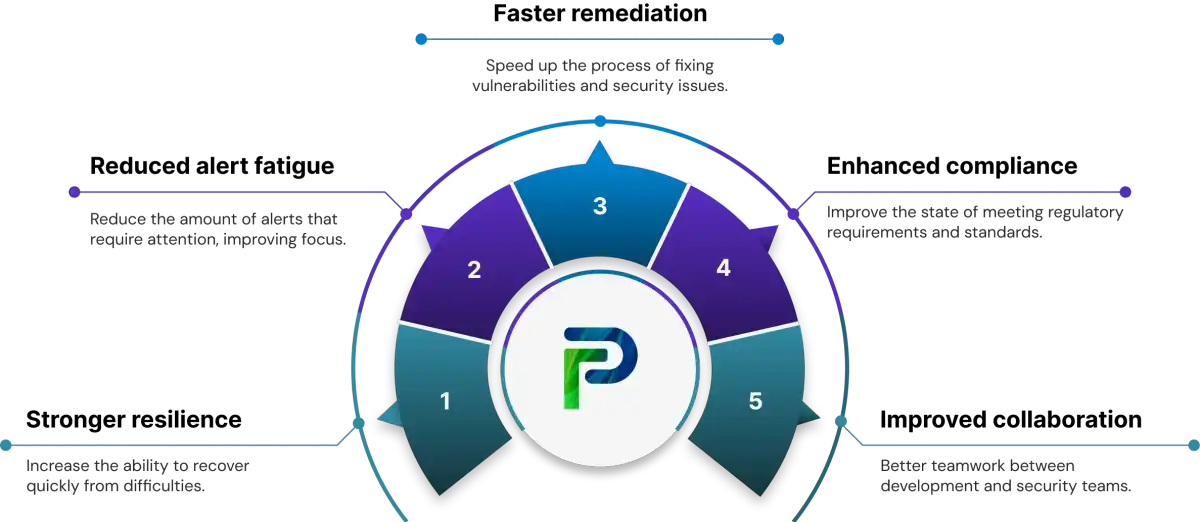
Benefits of ASPM for Enterprises
ASPM strengthens enterprise security, compliance, and DevSecOps velocity by bringing unified visibility, context, and control across the application lifecycle. It helps organizations reduce alert fatigue, accelerate remediation workflows, and foster seamless collaboration between security and development teams, all while reinforcing compliance and application resilience.
1. Reduced Alert Fatigue and Smarter Prioritization
Traditional AppSec tools flood teams with disconnected alerts that lack actionable context. ASPM changes this by correlating findings across code, pipelines, and cloud environments such as SAST, DAST, IaC, dependency, and runtime insights into a single source of truth.
By evaluating vulnerabilities through risk factors such as reachability, exposure, data sensitivity, and attack path potential, ASPM ensures that teams focus only on what’s actually exploitable. This context-driven approach minimizes noise, reduces fatigue, and drives faster, more confident responses.
2. Faster Remediation and Workflow Automation
ASPM streamlines remediation by automatically mapping findings to the right repositories, pipelines, and owners, similar to Zendesk’s ownership model. Security issues reach the responsible teams instantly, eliminating confusion and delay.
Integrated with CI/CD systems and developer tools, ASPM enables “shift left” practices, surfacing issues early in the SDLC without disrupting development velocity. Automation of triage, prioritization, and policy enforcement allows teams to remediate vulnerabilities in real time and sustain continuous delivery of secure applications.
3. Enhanced Compliance and Data Protection
Compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and CCPA demand continuous visibility into sensitive data and security posture. ASPM provides automated compliance checks, continuous monitoring, and detailed audit trails across applications.
By mapping application data flows, identifying PII, PHI, and PCI data stores, and verifying architectural controls, ASPM simplifies regulatory reporting and strengthens governance. It ensures that applications remain aligned with both internal policies and external compliance mandates.
4. Improved Collaboration Across Security and Dev Teams
ASPM bridges the long-standing gap between security and development by embedding contextual feedback directly into developer workflows. Developers gain real-time visibility into vulnerabilities with guidance for secure coding, while security teams maintain overarching control and traceability.
This shared visibility reduces rework, accelerates release cycles, and builds a stronger security culture where every contributor understands their role in maintaining application integrity.
5. Stronger Application Resilience and Business Continuity
By continuously monitoring architecture, configurations, and controls, ASPM helps organizations identify weaknesses before they escalate. It enforces standardized governance policies and validates application security posture over time, ensuring that resilience strengthens with every release.
Through proactive risk management, automated checks, and trend analysis, enterprises can safeguard against evolving cyberthreats and ensure uninterrupted user experiences.
6. Broader Business Impact and Executive Visibility
Beyond technical advantages, ASPM delivers measurable business outcomes. It provides executives with a holistic view of application risk posture, enabling data-driven decisions, effective resource allocation, and strategic planning.
Real-time dashboards and trend analytics transform security data into business insights, helping leaders demonstrate ROI, support compliance audits, and communicate clearly with boards and stakeholders. The result is improved brand reputation, customer trust, and long-term competitive advantage.
ASPM Tools & Vendors to Know
As the ASPM market evolves, several vendors are redefining how enterprises manage application security risk. Key evaluation factors include integration with existing DevSecOps tools, automation of vulnerability management, and scalability across hybrid environments.
Tech Prescient stands out as a forward-looking ASPM partner with strong capabilities in identity governance, data protection, and compliance automation. Its platforms like Identity Confluence unify visibility, automate policy enforcement, and simplify audits for frameworks such as SOC 2, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. By combining intelligent automation with deep security insight, Tech Prescient helps enterprises strengthen application posture and accelerate secure software delivery.
Real-World ASPM Use Cases
ASPM delivers tangible value across industries by unifying visibility, automating compliance, and strengthening resilience from code to cloud. Its continuous monitoring and contextual risk analysis make it indispensable for modern enterprises navigating complex hybrid environments.
1. Finance
Financial institutions use ASPM to reduce risk through strong segregation of duties (SoD) controls and continuous compliance enforcement. By integrating with existing security tools, ASPM ensures visibility into application vulnerabilities, automates audit reporting, and safeguards sensitive financial data to meet frameworks like SOX and PCI DSS.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, ASPM strengthens protection of PHI and ensures HIPAA compliance by continuously monitoring applications and APIs for misconfigurations or data exposure. Automated compliance reporting and drift detection help maintain an accurate security baseline, minimizing downtime during audits or recovery.
3. SaaS & Cloud
For SaaS and cloud-native organizations, ASPM enhances API security and software supply chain visibility. It maintains a live SBOM, detects vulnerabilities across CI/CD pipelines, and tracks third-party dependencies in real time. This visibility helps teams prioritize exploitable risks, secure APIs, and ensure rapid, compliant deployments.
Future of ASPM
As organizations continue to modernize applications and expand across hybrid and cloud-native environments, ASPM is becoming an essential layer of cybersecurity. It unifies visibility, risk management, and compliance across the entire application lifecycle, helping security teams move from reactive defense to proactive posture management. In the future, ASPM will evolve into an intelligent system that not only monitors vulnerabilities but also predicts, prevents, and automates responses to threats across code, pipelines, and cloud.
The next generation of ASPM solutions will focus on:
- AI-driven automation for faster and context-aware risk prioritization
- Predictive analytics to anticipate and mitigate emerging threats
- Seamless integration with DevSecOps tools for continuous protection
- Continuous compliance through automated policy checks and reporting
Forward-thinking vendors will lead this transformation by innovating rapidly, delivering regular updates, and maintaining transparent product roadmaps. ASPM is no longer a niche tool. It is the cornerstone of modern cybersecurity and a critical enabler of long-term resilience and security maturity in 2025 and beyond.
Final Thoughts
Application Security Posture Management (ASPM) is quickly becoming a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity. In a world where applications span code, pipelines, APIs, and cloud environments, ASPM brings clarity by unifying risks, streamlining compliance, and prioritizing what truly matters. It transforms fragmented security efforts into a cohesive strategy that not only reduces vulnerabilities but also empowers teams to act faster and smarter.
As organizations embrace DevSecOps, AI-driven automation, and Zero Trust principles, ASPM is evolving into an adaptive and intelligence-driven system. Its role goes beyond preventing breaches as it enables secure innovation, accelerates development, and builds long-term resilience.
To see how Tech Prescient helps enterprises adopt ASPM frameworks that balance security, compliance, and developer productivity-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does AI-SPM stand for?
AI-SPM stands for AI Security Posture Management. Think of it as a structured framework designed to secure AI systems end-to-end. It covers everything from protecting the AI models and datasets to monitoring pipelines and ensuring they are compliant with security best practices.2. How is AI-SPM different from CSPM?
While CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management) is mainly about securing cloud infrastructure, like fixing exposed S3 buckets, AI-SPM takes a more specialized role. It focuses on the unique risks tied to AI, such as adversarial model attacks, prompt injection, and securing data pipelines. Together, CSPM and AI-SPM complement each other but solve very different problems.3. What risks does AI-SPM address?
AI-SPM tackles the threats that traditional tools often miss. These include data poisoning, where malicious inputs corrupt AI training, prompt injection, which manipulates AI outputs, and misconfigurations in cloud-hosted AI systems. It also brings shadow AI deployments into visibility so organizations do not get blindsided by unmonitored models.4. Which industries need AI-SPM?
Any AI-driven organization can benefit, but it is especially critical in sectors like healthcare, finance, and SaaS. For example, AI-SPM helps prevent diagnostic data leaks in healthcare, safeguards fraud detection models in finance, and secures GenAI integrations in SaaS platforms. Essentially, if your business runs on AI, AI-SPM is your safety net.5. Is AI-SPM part of compliance management?
Yes, AI-SPM goes beyond security to ensure regulatory alignment. It maps directly to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO, helping enterprises prove compliance while reducing audit fatigue. By automating checks and documentation, it not only protects AI assets but also keeps organizations audit-ready at all times.